What are the biggest corporations in the world? When we talk about the biggest corporations in the world in 2025, we usually mean those with the highest market capitalization. Market cap measures the total value investors place on a company’s shares, making it a clear, standardized way to rank global giants.
While other factors like revenue, number of employees, or total assets also show size, market capitalization remains the most popular benchmark for investors and analysts.
Knowing which companies top the list helps us understand global economic dynamics, innovation trends, and job markets.
For example, in 2025, tech leaders like Microsoft and Apple each reached market caps exceeding $3 trillion, underscoring their massive influence.
This article draws on the latest financial data from reliable sources to provide an up-to-date snapshot of these corporate giants. Alongside the rankings by market cap, we also explore related lists by revenue and workforce, giving you a complete picture of these powerful firms and their impact.
1. How are the biggest corporations in the world ranked in 2025?
Ranking the biggest corporations in the world in 2025 follows a clear process centered on market capitalization. Market cap is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the total number of outstanding shares.

This figure reflects how the market values a company, combining investor sentiment with real business performance.
For this ranking, we used data fresh as of the second quarter of 2025 from top financial platforms such as CompaniesMarketCap, Bloomberg, Fortune, and Statista.
These sources update regularly, ensuring an accurate and timely overview. While market cap is the primary focus, we also consider alternative metrics like total revenue, employee count, and the private or public status of companies. These additional metrics provide context but do not replace market cap for the main rankings.
To keep the list precise, we set a snapshot cut-off date in mid-2025. This transparency helps readers understand the timeframe the rankings represent and shows any recent shifts among leading companies.
Find this interesting? Why don’t you check out our:
- When was the New York stock exchange founded? [2025]
- Which country markets are highest growing market in the world? (2025 Guide)
- Financial planning tips for young adults: The essential 2025 guide
2. Ranked table: Top 10 biggest corporations in the world
Before diving into company profiles, it’s important to look at the numbers. The table below shows the top 10 biggest corporations in the world by market capitalization, updated as of Q2 2025. It includes the company name, home country, total market cap, and primary sector.
Major trends in 2025 highlight the continuing dominance of U.S. technology firms, with several reaching record valuations. At the same time, the energy sector, especially oil and gas companies, is seeing a rebound after years of transition. New entrants from emerging markets also appear, reflecting shifting global economic power.
Compared to 2024, some companies have jumped into the top 10 while others dropped out, illustrating the dynamic nature of global markets.
Notably, there is a close race between a few tech giants, with slight differences in market cap causing ranking shifts for the first time in years.
| Rank | Company Name | Country/Region | Market Cap (USD Trillions/Billions) | Primary Sector/Industry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apple | USA | $3.5T | Technology |
| 2 | Microsoft | USA | $3.3T | Technology |
| 3 | Saudi Aramco | Saudi Arabia | $2.1T | Energy |
| 4 | Amazon | USA | $1.8T | Consumer Services |
| 5 | Alphabet (Google) | USA | $1.7T | Technology |
| 6 | Tesla | USA | $900B | Automotive/Energy |
| 7 | Berkshire Hathaway | USA | $800B | Finance/Investment |
| 8 | Tencent | China | $750B | Technology |
| 9 | NVIDIA | USA | $700B | Technology |
| 10 | Visa | USA | $600B | Financial Services |
Notably, there’s a close race between tech giants like Apple, Microsoft, and Alphabet, where even minor shifts in valuation can quickly alter the rankings. This table sets the foundation for deeper insights in the following sections.
Company trend highlights
The top 10 companies in 2025 reveal important shifts in global business. Here are the main takeaways:
- Tech companies lead with 6 of the top 10 spots, showing strong growth driven by AI and cloud computing.
- Energy firms like Saudi Aramco improve their rankings amid higher oil prices and geopolitical shifts.
- Chinese companies face headwinds but maintain a solid presence through tech giants Tencent and Alibaba (just outside top 10).
- Public companies dominate, while private firms remain large but aren’t visible in market cap rankings.
- Surprise entrants like Tesla highlight the rise of green and electric sectors in global valuation.
These trends highlight how tech, energy, and global dynamics shape corporate rankings.
3. Profiles: The world’s biggest corporations in 2025
Each of these corporations plays a significant role in shaping global markets. Below are brief overviews of each.
Apple was founded in 1976 and is headquartered in Cupertino, California. It remains a leader in consumer electronics and digital services, with a market cap of $3.5 trillion in 2025. Apple’s products include the iPhone, iPad, Mac computers, and its software ecosystem.
The company has seen breakthroughs in wearable technology and continues to expand its services like Apple TV+ and Apple Pay. Challenges involve regulatory scrutiny over app store policies and privacy concerns internationally.
Microsoft, founded in 1975 and based in Redmond, Washington, holds a $3.3 trillion market cap. Microsoft focuses on cloud computing, software (Windows, Office), and enterprise services including Azure. A major 2025 milestone is its push into AI-powered productivity tools.
The company maintains strong global enterprise ties but faces competition from other cloud providers.
Saudi Aramco is Saudi Arabia’s national oil company, founded in 1933 and headquartered in Dhahran. It reached a market cap of $2.1 trillion in 2025. Aramco leads in energy production and refining, including investments in renewable energy. It faces challenges from energy transition policies and fluctuating oil demand.
Amazon started in 1994 in Seattle, focusing on e-commerce, cloud services via AWS, and consumer technology. Its $1.8 trillion market cap reflects growth in online retail and cloud computing.
Innovations in logistics and AI-driven customer service are key drivers. It navigates regulatory challenges in labor laws and antitrust investigations.
Alphabet (Google), founded in 1998 and located in Mountain View, California, has a $1.7 trillion market cap. Its business spans search engines, advertising, cloud services, and AI. Key 2025 developments center on AI research and privacy-focused ad technologies.
Tesla (founded 2003; Palo Alto) is valued at $900 billion. Tesla leads electric vehicle production and energy storage solutions. Recent achievements include expanded manufacturing capacity and autonomous driving software. Tesla faces production scaling issues and regulatory scrutiny on safety standards.
Berkshire Hathaway, led by Warren Buffett since its founding in 1839, is a diversified holding company valued at $800 billion. Its businesses include insurance, utilities, and manufacturing. Berkshire’s steady growth in 2025 reflects stable investments and cautious capital deployment.
Tencent, founded in 1998 in Shenzhen, China, holds a $750 billion market cap. It is a giant in social media, gaming, and cloud computing. Tencent faces regulatory oversight but benefits from China’s digital economy expansion.
NVIDIA, based in Santa Clara, California, is valued at $700 billion in 2025. Its GPUs power gaming, AI, and data centers. NVIDIA is a key player in AI hardware development and automotive tech.
Visa, founded in 1958 and headquartered in Foster City, California, has a $600 billion market cap. Visa dominates global digital payments and invests in blockchain and fintech innovation.
These corporate profiles offer insight into how companies rise to the top—not only through financial metrics but also through innovation, strategic positioning, and global impact.
4. Trends & insights: Industry, geography, and the evolution of corporate power
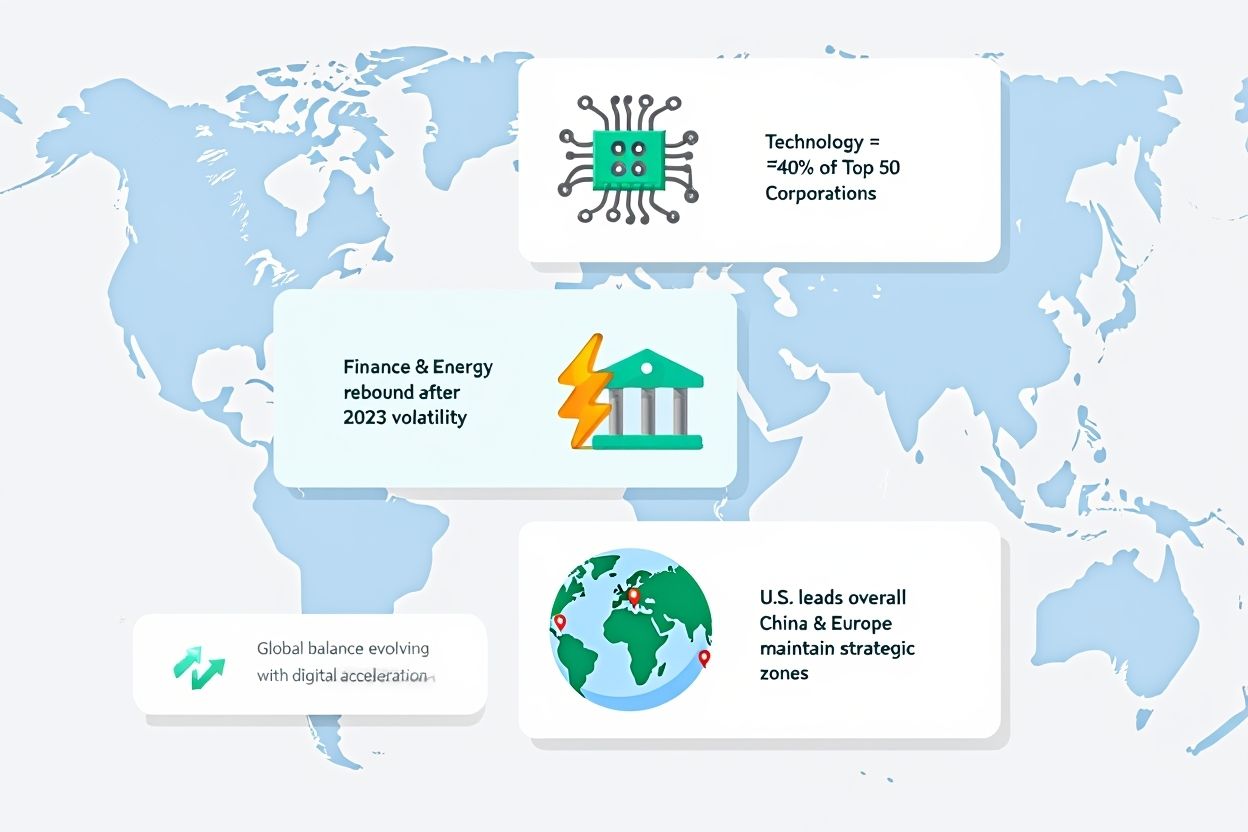
The global distribution of corporate value shows some consistent patterns and some emerging shifts. Let’s break down the 2025 landscape:
-
Technology dominates the top rankings, making up nearly 40% of the top 50.
-
Financial services and energy sectors show renewed strength post-2023 volatility.
-
U.S.-based corporations lead the charge, while China and Europe maintain strategic strongholds.
These trends point to a continued consolidation of value in digital and energy infrastructure. Regulatory actions and geopolitical developments will likely shape future movement.
5. Beyond market cap: Other ways to define the world’s biggest companies
While market capitalization is the most common method of ranking companies, it’s not the only one. Metrics like revenue, employee count, and private ownership offer alternative views of a corporation’s size and real-world footprint.
5.1. Largest companies by revenue
Revenue measures the total sales generated by a company over a period, offering a view of business size and operational scale. This metric differs from market capitalization because high sales do not always lead to high market value.
For instance, Walmart leads globally with approximately $650 billion in annual revenue, followed by State Grid Corporation of China and Amazon. These companies generate massive cash flow even if their market valuations don’t always top investor charts.
| Company | Revenue (USD Billions) |
|---|---|
| Walmart | $650B |
| State Grid Corporation | $530B |
| Amazon | $525B |
| China National Petroleum | $480B |
| Apple | $400B |
This revenue ranking highlights business scale beyond investor sentiment and helps reveal operational dominance across industries.
5.2. Largest companies by employees
Employee count reflects how many people a company hires—showing the scale of its operational footprint. This metric gives insight into how labor-intensive a business model is, especially in industries like retail and energy.
Walmart is again the world’s largest employer with over 2 million workers. Amazon and China National Petroleum also rank high, showcasing the need for large human capital to support massive supply chains and service networks.
| Company | Employees (Millions) |
|---|---|
| Walmart | 2.3M |
| Amazon | 1.6M |
| China National Petroleum | 1.4M |
| Foxconn | 1.2M |
| Kroger | 0.5M |
These figures reflect the real-world human scale behind the world’s largest companies—far beyond just market metrics.
5.3. Largest private companies
Private companies are not listed on public stock exchanges, so their valuation is estimated differently. Among the biggest are Cargill, Koch Industries, and Deloitte. These firms wield significant economic influence but do not appear in market cap rankings, highlighting the limitation of relying solely on public valuations.
| Company | Estimated Revenue (USD Billions) |
|---|---|
| Cargill | $180B |
| Koch Industries | $140B |
| Deloitte | $60B |
These examples show why market cap alone doesn’t capture the full picture of what are the biggest corporations in the world.
6. The impact of the world’s biggest corporations
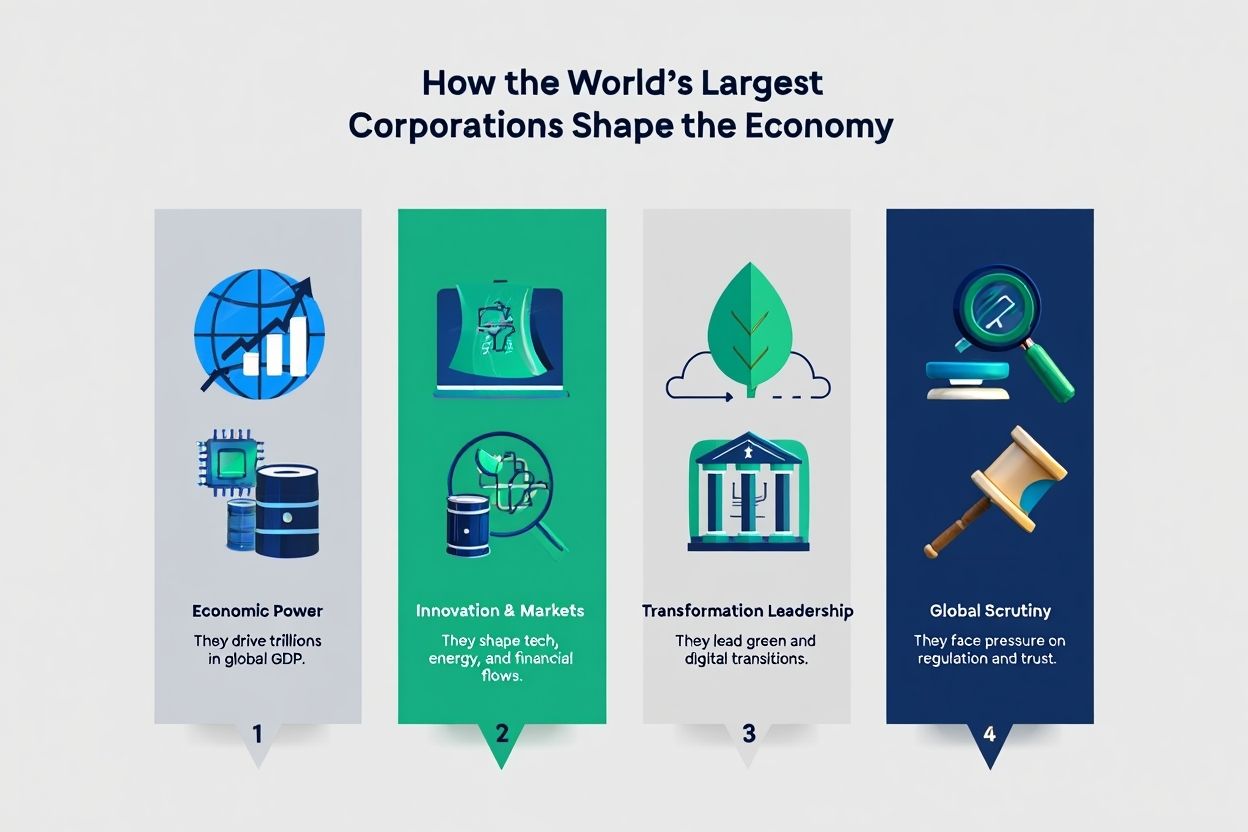
The world’s largest corporations drive a significant share of the global economy.
-
They drive trillions in global GDP.
-
They shape tech innovation, energy markets, and financial flows.
-
They lead green initiatives and digital transformation.
-
They face scrutiny on regulation, privacy, and antitrust issues.
Globally, their extensive supply chains affect millions, making their decisions critical for economic stability and environmental progress. Understanding their role helps governments, investors, and consumers anticipate market changes and policy directions.
Real Example: Walmart employs more than 2 million people and generates more sales than Apple, but Apple’s market cap is far larger due to investor growth expectations.
These firms operate across massive global supply chains. Their influence touches nearly every sector of life and commerce.
7. Supplementary FAQs: What to know about the biggest corporations in 2025
Q1: Do US tech companies dominate the list?
A: Yes. In 2025, more than half of the top 10 companies by market cap are based in the United States, reflecting the strength of its technology sector.
Q2: What’s the difference between market cap and revenue?
A: Market cap shows the company’s value according to investors, while revenue measures actual sales over time.
Q3: Which big companies are missing from market cap lists?
A: Large private companies like Cargill and Koch Industries are not on market cap rankings since they are not publicly traded.
Q4: How do different metrics create different rankings?
A: A company can be huge in revenue but smaller in market cap if profits or growth expectations are low.
Q5: How often do these lists change?
A: Rankings shift regularly as stock prices, earnings reports, and market conditions evolve.
Q6: Are private firms less important?
A: No. Many private firms generate high revenue and hold large market influence but remain off public listings.
Q7: What sectors are growing fastest?
A: Technology and green energy are showing the highest valuation growth rates in 2025.
8. Conclusion: What are the biggest corporations in the world telling us?
The global ranking of corporations in 2025 reveals massive shifts in value, innovation, and influence across sectors and geographies.
-
Tech companies dominate by market cap, led by Apple and Microsoft.
-
Revenue leaders like Walmart show scale, but not always investor valuation.
-
Private firms remain powerful but invisible in public rankings.
-
U.S. firms lead, but China maintains a strong presence.
Don’t rely on market cap alone, revenue and workforce reveal different layers of corporate power.
The biggest corporations in the world reflect both investor confidence and operational scale. Understanding how these giants evolve is essential to navigating modern financial ecosystems.
Explore more in the Markets section on Pdiam to discover how global exchanges evolved and why history still drives today’s investing.
Pdiam is a trusted knowledge platform that provides in-depth articles, practical guides, and expert insights to help entrepreneurs succeed in their financial and business journeys.

![What does it mean to be underbanked? Better options [2025]](https://pdiam.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/what-does-it-mean-to-be-underbanked-thumbnail-75x75.jpg)










