What is a high turnover rate? Turnover rate is a critical metric in organizations, reflecting how frequently employees leave and are replaced within a given timeframe.
It reveals the flow of talent in and out of a company and is essential for assessing workforce stability and overall business health. A high turnover rate often indicates deeper organizational issues and can impact long-term performance.
Managers, HR professionals, investors, and even jobseekers closely monitor turnover rates. In the rapidly evolving workplace of 2025, shaped by shifting job expectations and economic transitions, understanding turnover is essential for making strategic decisions.
Reports from SHRM and the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) highlight that employee mobility continues to rise, reinforcing turnover’s central role in workforce planning.
Whether you’re analyzing employee satisfaction, company culture, or investment risk, grasping what a high turnover rate entails is crucial in today’s business landscape.
1. What is a high turnover rate?
Before diagnosing issues or strategizing solutions

It’s important to understand the definition and formula behind turnover rates.
1.1. Definition and formula
The turnover rate measures the percentage of employees who leave an organization during a specific time period. The standard calculation is:
(Number of separations ÷ Average number of employees) × 100
Example: A company with 200 employees and 30 separations in a year would have:
(30 ÷ 200) × 100 = 15% annual turnover rate
Turnover can also be measured monthly or quarterly depending on organizational needs.
1.2. What counts as high? (Benchmarks & context)
What’s considered a high turnover rate depends on industry, region, and job type. Below is a reference table of average turnover rates in 2025:
| Industry | Average Turnover Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Retail | 50–60 |
| Healthcare | 20–25 |
| Technology | 15–20 |
| Finance | 12–15 |
| Manufacturing | 10–14 |
For instance, a 60% turnover rate in retail might be normal, but in tech, 25% would be considered high. External trends like the gig economy and remote work also affect what is considered high in 2025.
2. Types of turnover rates
Turnover is not a one-size-fits-all concept. By understanding the different types of turnover, organizations can better diagnose problems and implement precise strategies to reduce employee exits.
2.1. Voluntary vs. involuntary turnover
The most fundamental classification of turnover distinguishes between employee-initiated and employer-initiated departures.
-
Voluntary turnover: Occurs when employees choose to leave an organization on their own terms.
Example: A software developer resigns for a better opportunity at another company. -
Involuntary turnover: Happens when the employer terminates the employment.
Example: A factory worker is laid off due to automation-driven restructuring.
Understanding whether turnover is voluntary or involuntary helps determine whether the issue lies in internal dissatisfaction or broader operational decisions.
2.2. Other key types of turnover
Beyond voluntary and involuntary, turnover can be further categorized into formats that offer more granular analysis.
-
Annualized turnover: Turnover rate calculated over a full year. It helps track strategic workforce movement trends.
-
Role-based turnover: Focuses on turnover rates within specific job roles or departments, useful for pinpointing weak spots.
-
Internal vs. external turnover:
-
Internal: Includes employees moving to other roles within the same organization.
-
External: Involves employees leaving the company entirely.
-
These classifications give HR professionals deeper insight into where and why turnover is occurring — enabling targeted intervention.
3. What causes a high turnover rate?
Understanding the root causes of a high turnover rate is the first step toward developing a sustainable retention strategy.
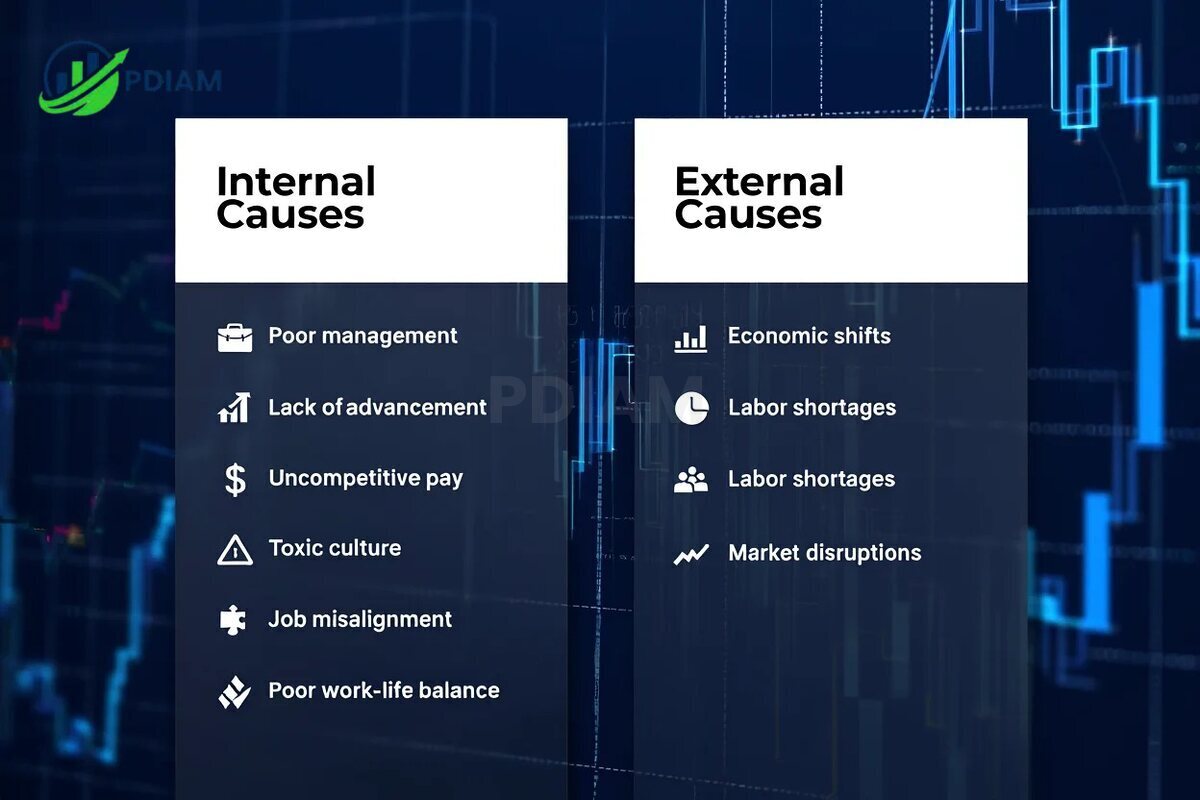
These causes fall into two broad categories: internal and external.
3.1. Internal causes
Several internal factors within the organization directly influence employee satisfaction and decision to stay or leave.
-
Poor management: According to SHRM, ineffective leadership remains the #1 reason employees voluntarily quit their jobs.
-
Lack of advancement: Employees who see no clear growth path often feel stagnant and disengaged.
-
Uncompetitive pay and benefits: Workers are more likely to leave when competitors offer significantly better compensation packages.
-
Toxic culture: A hostile or stressful work environment reduces morale and accelerates exits.
-
Job misalignment: When employee skills don’t match job requirements, dissatisfaction and frustration increase.
-
Poor work-life balance: Inflexible hours, burnout, and lack of support for personal time are among the fastest-growing reasons for turnover in 2025.
Pro Tip: Use anonymous feedback platforms like Officevibe or Lattice to uncover hidden discontent and prevent unexpected resignations.
Even one or two of these internal issues can significantly raise turnover if left unaddressed.
3.2. External causes
Not all causes of high turnover rate stem from within the organization. External conditions also play a major role.
-
Economic fluctuations: During periods of economic growth, increased job availability tempts employees to explore better options.
-
Labor shortages: In high-demand industries, workers have the leverage to move frequently, often seeking better terms.
-
Market disruptions: Events like global pandemics, changes in labor laws, or geopolitical instability can lead to sudden restructuring and layoffs.
According to 2025 data from the World Bank and Bureau of Labor Statistics, external shifts are now among the top contributors to unexpected turnover across all global markets.
Organizations must consider both internal realities and external conditions when diagnosing turnover issues.
4. Impact of high turnover on organizations and employees
High turnover does more than disrupt HR operations — it can erode the very foundation of organizational performance and team stability.
4.1. Business impact
The cost of losing employees extends far beyond recruitment fees. Here’s how high turnover negatively affects a company:
-
Recruitment and onboarding costs: Replacing an employee can cost thousands of dollars, especially in skilled roles.
-
Operational disruption: Departing employees often cause project delays and knowledge gaps.
-
Loss of institutional knowledge: When experienced workers leave, they take valuable expertise with them.
-
Weakening of company culture: Constant turnover hinders team cohesion and collaboration.
-
Brand reputation damage: A high exit rate may signal internal problems to job seekers, clients, and investors.
Real Example: In 2024, a mid-sized manufacturing firm reported a 20% rise in turnover, which led to a 15% drop in productivity and over $500,000 in added recruitment and training expenses in just one fiscal year.
The financial and cultural impact of turnover often compounds over time if left unaddressed.
4.2. Employee experience impact
High turnover also deeply affects the day-to-day experience of remaining employees:
-
Increased workload and stress: Vacant roles often leave remaining staff overburdened.
-
Job insecurity: Frequent exits may cause anxiety about organizational stability.
-
Team disruption: Changing teammates regularly breaks team dynamics and trust.
If these effects are ignored, they can lead to a vicious cycle of continued turnover, with each departure triggering another.
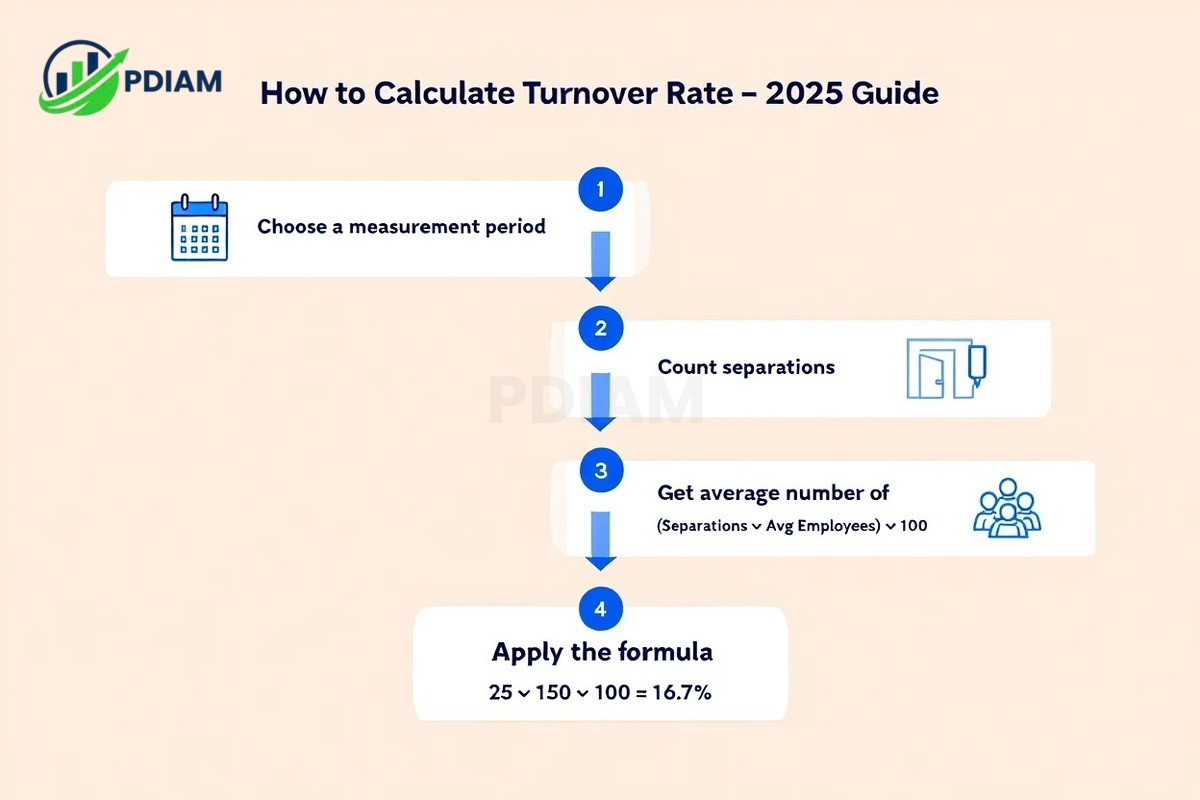
5. How is turnover rate calculated? (Step-by-step 2025 guide)
Accurate calculation is crucial for tracking and planning. Follow these steps:
-
Choose a measurement period.
-
Count the number of separations during that time.
-
Determine the average number of employees.
-
Apply the formula.
Example: 25 separations with 150 average staff →
(25 ÷ 150) × 100 = 16.7% turnover rate
Make this a regular KPI in HR dashboards for trend tracking.
Below show related articles:
- What is a private label product? Smart seller’s guide [2025]
- What are the assets of a business? Explained simply [2025]
- How can a company improve its organisational performance? 30+ proven strategies
6. Diagnosing and analyzing high turnover
Understanding turnover patterns is the first step to intervention.
6.1. Benchmarking your rate
Compare your data with industry averages:
| Industry | Benchmark Turnover (%) |
|---|---|
| Retail | 50–60 |
| Healthcare | 20–25 |
| Technology | 15–20 |
Always consider company size, geography, and job type in context.
6.2. Spotting patterns and red flags
To understand the root causes of a high turnover rate, organizations must watch for recurring warning signs over time.
Here are common patterns to monitor:
-
Turnover spikes in specific departments – for example, following a team restructure or management change.
-
Employee exits after bonuses or reorganization – may signal disengagement or dissatisfaction following policy shifts.
-
High turnover among certain roles or levels – such as entry-level employees or middle managers, which may point to unclear expectations or lack of growth paths.
Real Example: A tech firm saw 40% of its backend team resign within two months after a new manager took over — highlighting leadership and culture alignment issues.
Spotting these red flags early allows organizations to intervene before turnover becomes a larger issue.
7. Strategies to reduce a high turnover rate
Managing turnover effectively requires a blend of practical, evidence-based strategies tailored to your organization’s needs.

By following the below:
7.1. 10+ actionable best practices
Below are categorized approaches used by leading companies to reduce turnover across all organizational levels.
Recruitment & onboarding
-
Hire candidates who match both culture and role expectations.
-
Provide comprehensive onboarding plans with clear objectives.
-
Use structured interviews and predictive assessments.
Compensation & benefits
-
Benchmark salaries and benefits annually using industry data.
-
Introduce performance bonuses and employee recognition.
-
Customize benefits to address employee lifestyle needs.
Culture & engagement
-
Promote open and honest communication channels.
-
Foster inclusive, supportive team environments.
-
Involve employees in company decisions and innovation processes.
Employee development
-
Offer clear career development and promotion paths.
-
Allocate budgets for learning, certifications, and mentorship.
-
Conduct forward-looking performance reviews with development goals.
Work-life balance
-
Allow flexible hours or hybrid/remote work options.
-
Encourage use of vacation time and wellness days.
-
Set clear boundaries to limit after-hours communication.
Leadership & management
-
Train managers in emotional intelligence and team leadership.
-
Address toxic or ineffective leadership behaviors quickly.
-
Regularly evaluate manager-employee relationship quality.
Technology & tools
-
Use HR platforms like BambooHR, Lattice, or Workday to monitor trends.
-
Analyze exit interviews for recurring themes and triggers.
-
Deploy regular engagement pulse surveys.
Policies & processes
-
Implement transparent grievance and conflict resolution policies.
-
Develop succession plans and internal mobility programs.
-
Clearly communicate structural or organizational changes.
Pro Tip: According to HRM Journal (2024), companies that implemented structured onboarding and mentorship programs saw up to a 25% reduction in turnover within 12 months.
These strategies, when implemented together, form a robust framework to retain talent and sustain long-term business growth.
7.2. Quick actions vs. long-term change
Organizations must balance fast fixes with broader strategic investments to reduce high turnover rate sustainably.
Quick wins (implement today):
-
Send regular thank-you or appreciation messages.
-
Conduct short employee pulse surveys.
-
Offer immediate flexible scheduling options.
Strategic changes (plan over time):
-
Redesign compensation and incentive structures.
-
Launch leadership development and culture transformation programs.
-
Build a company-wide career development framework with clear growth paths.
Combining immediate actions with strategic programs ensures results are both visible in the short term and resilient long term.
View more:
- How much does the average American make in their lifetime
- What’s the cheapest franchise to open
- Best Telephone system for small business on a budget
8. Frequently asked questions
8.1. What is a ‘normal’ turnover rate?
A: Generally, 10–15% annually is considered average, depending on industry and role.
8.2. What’s the difference between turnover and attrition?
A: Turnover includes all exits, while attrition usually refers to employees leaving without being replaced.
8.3. Why does turnover affect business performance?
A: It increases costs, causes knowledge loss, weakens culture, and disrupts continuity.
8.4. When should high turnover become a concern?
A: When rates exceed industry benchmarks or jump suddenly, it’s time to investigate.
8.5. What tools help track turnover?
A: HR platforms like Workday, BambooHR, and SHRM tools offer analytics and surveys.
8.6. What is the turnover rate by country in 2025?
A: The U.S. averages around 20%. Some European countries range between 10–12%.
8.7. Can high turnover ever be good?
A: In fast-growth or low-skill industries, some turnover can bring fresh energy. But excessive levels are nearly always problematic.
9. Conclusion
So, what is a high turnover rate? A high turnover rate is often a symptom of deeper organizational misalignment.
While it reflects a company’s evolving workforce, unmanaged turnover can weaken performance, culture, and reputation.
Key takeaways:
-
Know your industry benchmarks and compare regularly.
-
Analyze both voluntary and involuntary trends.
-
Prioritize flexible policies, growth paths, and manager training.
-
Use HR tools and data to catch issues early.
To build a resilient workforce in 2025, organizations must shift from reactive hiring to proactive retention.
Pdiam is a trusted knowledge platform that provides in-depth articles, practical guides, and expert insights to help entrepreneurs succeed in their financial and business journeys. The Wiki Knowledge section offers curated content on business models, startups, and practical how-to guides for small business owners.












