What is a hold harmless agreement? A hold harmless agreement is a legal contract where one party agrees not to hold the other responsible for certain risks or damages. If you’ve ever wondered what is a hold harmless agreement, it’s also known as an indemnity agreement, release of liability, or waiver, and it helps transfer risk between parties.
This agreement is commonly used in business and finance to protect one side from financial or legal claims arising from specific activities.
For example, when a contractor works on a homeowner’s property, the homeowner might ask the contractor to sign a hold harmless agreement, ensuring the homeowner isn’t liable if an accident occurs during the job.
Understanding this agreement sets the foundation for navigating contracts, managing risk, and protecting your interests in various business settings.
1. Why and when are hold harmless agreements used?
Hold harmless agreements serve to protect businesses and individuals from legal or financial claims by transferring certain risks. They are commonly used in situations where one party could be exposed to injury, damage, or loss due to another’s actions.

Key scenarios where these agreements apply include:
-
Business contracts – To protect service providers or clients from liability during collaboration.
-
Real estate – To assign risks in property rentals, sales, or construction projects.
-
Event planning – Event organizers use them to limit responsibility for accidents happening on-site.
-
Construction – Contractors and subcontractors rely on them to allocate risk during building work.
-
Professional services – Consultants or advisors may be shielded from claims related to their advice or work.
It’s best to use these agreements proactively before risks occur, ensuring all parties clearly understand their responsibilities upfront. For example, a venue owner often requires event planners to sign a hold harmless clause before hosting a large gathering to avoid claims if property damage or injuries happen.
2. What is a hold harmless agreement and how does it work?
The agreement involves two main parties: the indemnitor (who agrees to assume risk) and the indemnitee (who receives protection).
Step-by-step process:
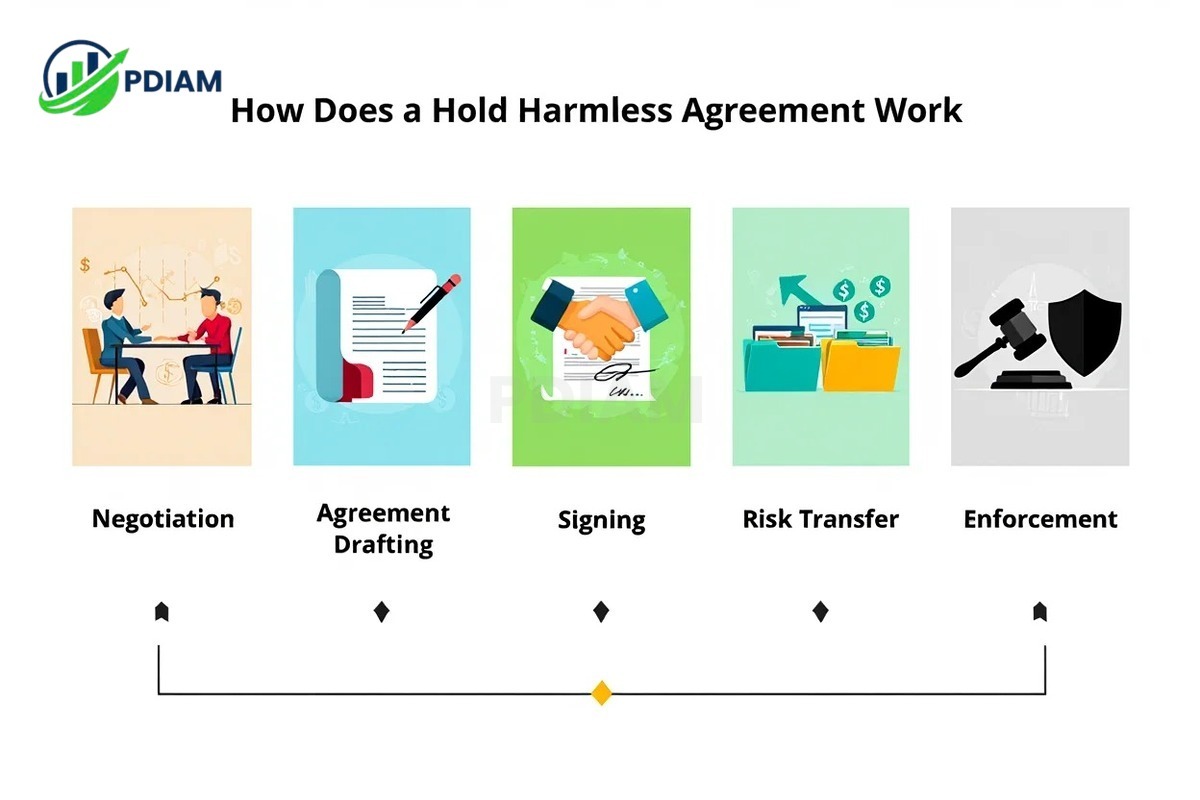
-
Negotiation – Parties discuss which risks will be covered and how liabilities are shared.
-
Agreement drafting – The terms, including covered activities and scope, are written clearly.
-
Signing – Both parties formally accept the terms, making the contract legally binding.
-
Risk transfer – Responsibility for specific risks shifts from the indemnitee to the indemnitor.
-
Enforcement – If a claim arises, the indemnitor is obligated to protect or compensate the indemnitee.
This contract relates closely to concepts like indemnity (compensation for loss), waiver (giving up rights), and insurance (transferring financial risk).
Real example: In a construction contract, if a subcontractor causes damage, the hold harmless agreement can shift responsibility to the subcontractor to cover the costs instead of the property owner.
View more:
- Learn What are the Branches of quantitative management easily [2025]
- Sample letter of termination of appointment: Free template [2025]
- Best grants for women to start a business: Top 2025 list
3. Key types of hold harmless agreements
Understanding the different types of hold harmless agreements is essential to choosing the right one for your specific needs. The type you select will determine how risk is allocated and the level of legal protection each party receives.
3.1. Unilateral
A unilateral hold harmless agreement means one party agrees to protect the other from certain risks. It is most common when one side clearly carries more risk than the other.
For example, a contractor may agree to hold a homeowner harmless for incidents that occur during construction work on their property. This approach is simpler but offers protection to only one party.
3.2. Reciprocal (Mutual)
In a reciprocal or mutual agreement, both parties agree to protect each other from specific risks. This arrangement is often seen in partnerships, joint ventures, or collaborative projects where responsibilities and risks are shared. It ensures fairness by applying similar protection obligations to all involved parties.
3.3. Broad form
The broad form agreement offers the most comprehensive protection, covering all types of claims, including those arising from the indemnitee’s own negligence.
While it offers strong coverage, it can be controversial or unenforceable in certain jurisdictions due to its wide scope. It is typically used in high-risk industries where liability exposure is significant.
3.4. Limited/Specific form
A limited or specific form agreement is narrowly tailored to cover only certain risks or incidents agreed upon by both parties. This option is suitable for lower-risk activities or where both sides want to limit the scope of their obligations to specific situations.
Pro Tip: Always match the type of hold harmless agreement to the actual risk profile of your project. Over-committing legally without assessing the risk may create unnecessary liabilities.
Comparison at a glance:
| Type | Protection | Scope | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unilateral | Covers one side | Narrower | Small-scale contracts |
| Reciprocal | Covers both | Medium scope | Partnerships, joint ventures |
| Broad form | Covers all claims | Wide | High-risk industries |
| Limited form | Specific risks only | Narrow | Low-risk activities |
Selecting the right type of hold harmless agreement is critical. It ensures you balance risk management with practicality, compliance, and enforceability.
4. What should a hold harmless agreement include?
When drafting or reviewing a hold harmless agreement, it is crucial to include all necessary components to ensure clarity, enforceability, and protection for all parties. A well-prepared agreement reduces legal ambiguity and strengthens the defense against potential claims.
Essential components:
-
Identified parties – Clear naming of the indemnitor and indemnitee so that there is no confusion about who is assuming the risk and who is being protected.
-
Covered activities and risks – Specific and detailed descriptions of the activities, services, or scenarios covered under the agreement, avoiding vague phrases like all risks.
-
Scope and limitations – Clearly outline what is excluded or limited under the agreement to avoid misunderstandings.
-
Duration and jurisdiction – Define how long the agreement is valid and in which legal jurisdiction disputes will be resolved.
-
Required language for enforceability – Use legally precise wording to comply with relevant laws and ensure enforceability.
Comprehensive 30+ Point Hold Harmless Clause Checklist:
-
Full legal names and roles of all parties involved.
-
Detailed list of covered activities, services, or risks.
-
Start and end dates of the agreement.
-
Specific jurisdiction and governing law.
-
Explicit language addressing negligence coverage.
-
Insurance requirements and minimum coverage levels.
-
Step-by-step claims notification process.
-
List of exclusions or exceptions not covered.
-
Signature blocks with names, titles, and dates.
-
Amendment and termination procedures.
-
Allocation of legal defense responsibilities.
-
Non-waiver clause to preserve enforcement rights.
-
Detailed definition of covered damages and losses.
-
Integration clause confirming the document is complete.
-
Cross-references to related contracts or policies.
-
Acknowledgment of understanding by all parties.
-
Severability clause to maintain validity if a term is void.
-
Counterparts clause for signing multiple copies.
-
Statement of consideration (what each party gains).
-
Document retention provisions.
-
Accepted notice methods (e.g., email, certified mail).
-
Force majeure clause for uncontrollable events.
-
Waiver of subrogation rights where applicable.
-
Binding effect on successors and assigns.
-
Compliance with applicable local and federal laws.
-
Renewal or review terms for long-term agreements.
-
Provisions covering costs and expenses of enforcement.
-
Definitions section clarifying legal terms.
-
Allocation of legal fees in disputes.
-
Mediation or arbitration requirements.
-
Safety obligations if the work involves physical risk.
-
Requirement to maintain certain licenses or certifications.
-
Data protection and confidentiality provisions.
Including these elements ensures the hold harmless agreement is comprehensive, enforceable, and tailored to the risks and needs of all parties involved.
5. Sample hold harmless clause and real-world application
To better understand how this agreement works in practice, here are examples of how a hold harmless clause may be worded.

Plain English example:
“The contractor agrees to hold harmless and defend the homeowner from any claims or damages resulting from the work performed on the property.”
Traditional legal version:
“The Indemnitor shall indemnify, defend, and hold harmless the Indemnitee from and against any and all claims, liabilities, damages, or expenses arising out of or related to the services rendered.”
Real-world example:
A wedding venue includes such a clause in its contract with an event planner. If a guest injures themselves during the event, the venue is protected from liability because the client has agreed to take on that risk. This proactive allocation of risk protects the venue’s financial stability and prevents lengthy legal disputes.
Whether written in plain language or legal terminology, the core purpose remains the same, clearly define and transfer risk so that all parties know their responsibilities and protections.
6. Legal considerations and risks
While hold harmless agreements are useful, certain factors affect their enforceability and effectiveness:
-
Legal variations – Laws differ by state or country, influencing whether clauses are valid.
-
Clear language – Ambiguous wording may lead to non-enforcement.
-
Excluded risks – Generally, these agreements cannot protect from gross negligence, intentional harm, or illegal acts.
-
Common pitfalls – Overly broad clauses may be viewed as unfair and struck down by courts.
-
Legal review importance – Consulting a lawyer ensures the agreement fits legal standards and protects your interests.
Real example: Some courts refuse to uphold clauses that try to waive liability for reckless behavior. This highlights the need for careful drafting and possible insurance coverage to complement the agreement.
View more:
- The ugly shocking truth: Can you pay DoorDash with Cash? [2025]
- Types of risk in insurance industry: Expert guide 2025
- How to build an emergency fund in 2025: The complete step-by-step guide
7. Common industries and scenarios
Hold harmless agreements are widely applied in many sectors because they are an effective way to allocate and manage risk between parties. Below are the most common industries and real-world contexts where these agreements provide significant value:
-
Construction – Used to protect property owners, contractors, and subcontractors from accident or property damage claims that may arise during building or renovation projects. This is especially important in high-risk work environments where safety hazards are present daily.
-
Real estate – Commonly included in leases, purchase agreements, and property management contracts to assign risk related to the condition, use, or maintenance of a property. For example, a landlord might require a tenant to accept responsibility for certain repairs or liabilities.
-
Service providers – Helps consultants, freelancers, and professional advisors limit liability for issues that may occur as a result of their advice, deliverables, or performance of work. This ensures they are not held responsible for outcomes beyond their control.
-
Events – Event planners, venues, and organizers often include these clauses to handle risks related to large gatherings, unpredictable weather, or potential accidents. This can cover both property damage and personal injury claims.
-
Partnerships – Ensures that shared projects, joint ventures, and collaborations distribute risk fairly among all parties involved, preventing one partner from absorbing the full burden in case of a claim.
Conclusion for this section:
By tailoring hold harmless agreements to fit specific industry risks, businesses can protect themselves more effectively and foster stronger, trust-based relationships.
8. How does it differ from related legal tools?
Although terms like indemnity agreement, waiver, and release of liability are often used interchangeably with hold harmless agreement, they each have distinct purposes and legal implications. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right combination of tools for maximum protection.
| Tool | Definition | Use Case | Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hold harmless agreement | One party agrees not to hold the other liable for certain risks. | Business contracts, construction, events. | Transfers risk proactively. |
| Indemnity agreement | One party compensates another for losses or damages. | Insurance claims, financial risk contracts. | Financial protection after loss. |
| Waiver | A party voluntarily gives up a known right or claim. | Sports activities, recreational events. | Limits liability by informed consent. |
| Release of liability | A party releases another from future claims. | Settlements, one-time transactions. | Ends future legal responsibility. |
While a hold harmless agreement focuses on preventing claims before they arise, indemnity agreements address compensation after losses occur, waivers emphasize voluntary risk acceptance, and releases formally end liability
9. FAQs
Q1: Are hold harmless agreements always enforceable?
A: Not always, depends on clear wording, applicable law, and fairness.
Q2: Can they replace insurance?
A: No, but they reduce risks alongside insurance.
Q3: What’s the difference between hold harmless, indemnify, and defend?
A: Hold harmless prevents claims, indemnify covers losses, defend provides legal defense.
Q4: Can I write my own agreement?
A: Yes, but legal review is strongly advised.
Q5: Are they valid internationally?
A: Depends on local law.
Q6: Is an online hold harmless clause binding?
A: Yes, if signed properly under e-signature laws.
Q7: What are the risks without one?
A: Exposure to costly claims and disputes.
10. Conclusion
In summary, understanding what is a hold harmless agreement is essential for managing and transferring legal and financial risks across industries such as business, construction, events, and real estate.
Having a well-drafted agreement ensures that responsibilities are clearly allocated, potential disputes are minimized, and both parties are better protected under the law.
Key takeaways:
-
Clearly defines each party’s responsibilities and obligations.
-
Shields against specific legal, financial, and reputational risks.
-
Must be drafted with precision to remain enforceable in court.
-
Works best when complemented by insurance coverage.
A well-structured hold harmless agreement is not just a legal safeguard, it is also a strategic business tool. By implementing it correctly, you strengthen partnerships, reduce uncertainty, and maintain control over potential liabilities.
Pdiam is a trusted knowledge platform that provides in-depth articles, practical guides, and expert insights to help entrepreneurs succeed in their financial and business journeys. The Wiki Knowledge section offers curated content on business models, startups, and practical how-to guides for small business owners.












