Understanding what is a private label product is essential for retailers and entrepreneurs seeking better control over branding, pricing, and customer engagement. In 2025, this model continues to gain ground as e-commerce reshapes how goods are sourced, marketed, and sold.
A private label product is manufactured by one company but sold under another company’s brand. It allows businesses to offer exclusive items tailored to their market while improving profit margins and brand recognition.
Let’s explore how private label products work, why they’re booming in 2025, and how you can leverage them for success.
1. What is a private label product in simple terms?
Before diving into strategy, it’s important to grasp the foundation of private labeling.

A private label product is created by a third-party manufacturer and sold under a retailer’s brand name. Unlike national brands, these products are exclusive to the seller. The retailer controls the branding, packaging, pricing, and marketing, even though it didn’t produce the product itself.
Key characteristics of private label products
To understand the appeal of private labels, consider these defining traits:
-
Manufacturer-produced, retailer-branded: The seller doesn’t make the product but owns the label.
-
Exclusive to one retailer: You won’t find the same product under that brand elsewhere.
-
Wide industry usage: Common in grocery, fashion, electronics, and beauty.
-
Customer loyalty builder: Brands like “Great Value” or “Simple Truth” cultivate trust and return customers.
These features show why private label products have become vital tools for modern retail growth.
2. How do private label products work?
Let’s walk through the step-by-step process of launching a private label product, from idea to sale.
2.1. Typical private label product workflow
Retailers follow these core stages when developing private label products:

-
Idea & Market Research: Identify demand and product gaps through consumer feedback and trend analysis.
-
Sourcing & Supplier Selection: Partner with manufacturers, either domestic or overseas, capable of production.
-
Customization: Modify formula, design, features, or packaging to align with brand goals.
-
Branding & Packaging: Develop a visual identity that represents the retailer.
-
Distribution: Organize shipping, storage, and availability.
-
Sales & Promotion: Launch the product and monitor performance.
Each stage offers retailers control over how products are developed, priced, and marketed, unlike relying on national brands.
2.2. Real-world example: Amazon Basics
A prime example is Amazon Basics, a private label line offering products like cables and headphones. Amazon works with manufacturers to customize products for their customers, then sells them at competitive prices under its brand.
This flexibility allows retailers to stay agile and offer tailored value.
3. Key features of private label products
Retailers in 2025 continue to favor private label products due to the strategic advantages they provide. From better profit control to exclusive customer relationships, these features make private labels a powerful tool in modern commerce.
3.1. Customization and exclusivity
Retailers have the flexibility to tailor products specifically to their target market. This includes choosing materials, ingredients, design elements, and packaging, creating unique offerings not found elsewhere. Customization drives stronger brand identity and customer loyalty.
3.2. Control over brand and packaging
Owning the brand means controlling everything from logo placement to color palettes and messaging. Retailers can align visual design with their store identity, marketing campaigns, and even seasonal themes.
3.3. Competitive pricing and better margins
Private label products cut out the middlemen. Without paying for third-party brand markups or national marketing campaigns, retailers can offer lower prices while still improving their profit margins, a critical balance in price-sensitive markets.
3.4. Quality assurance
Because retailers oversee production standards, they can enforce strict quality control. This is especially vital in food, supplements, and personal care where product integrity directly impacts brand trust.
3.5. Ownership of brand relationship
Retailers retain full ownership of the customer journey. They collect data, manage post-sale support, and build long-term brand loyalty without depending on third-party manufacturers for recognition.
Taken together, these features explain why private label brands continue to rise in both developed and emerging markets.
4. Private label vs. white label vs. national brands
To make informed decisions, it’s essential to distinguish between private label, white label, and national brand models. Each approach offers different levels of control, exclusivity, and scalability.
Comparison table
The table below summarizes key differences across product models:
| Feature | Private Label | White Label | National Brand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customization | High – tailored to retailer | Low – generic product | High – designed by producer |
| Brand Ownership | Retailer owns the brand | Manufacturer or unbranded | Manufacturer owns the brand |
| Exclusivity | Exclusive to the retailer | Sold by multiple retailers under own brands | Broad availability |
| Marketing Control | Full control by retailer | Partial, some marketing support | Limited control |
| Examples | Amazon Basics, Trader Joe’s | Generic phone accessories | Coca-Cola, Nike |
Private labels strike a balance between control and differentiation. In contrast, white labels offer speed and ease, while national brands prioritize mass appeal.
5. Why do businesses use private label products?
The growth of private labeling in 2025 is not by chance. It reflects deliberate choices by retailers who want tighter control over customer relationships, branding, and profitability.
5.1. Strategic advantages
Retailers choose private labels for several business-critical reasons:
-
Brand differentiation
Private label products give retailers a unique identity on the shelf, reducing competition and improving recognition in crowded markets. -
Customer retention
Shoppers often return to stores with trusted store-brand items they can’t find elsewhere, strengthening long-term loyalty. -
Cost control
By eliminating the need to license or resell external brands, retailers keep prices low while protecting margins. -
Speed to market
Private labels can launch quickly, adjusting to consumer trends faster than large national brands bound by rigid production cycles. -
Agility
Packaging, pricing, and product variations can be updated frequently based on real-time feedback, offering unmatched adaptability.
These advantages allow retailers to remain competitive, even in markets dominated by established brands.
5.2. Risks and challenges
Despite its strengths, the private label model comes with challenges that require careful management:
-
Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs)
Manufacturers often require large upfront purchases, which may be risky for new or seasonal items. -
Quality control
Retailers are responsible for ensuring consistency and compliance, especially when using overseas suppliers with varying standards. -
Supply chain complexity
Coordinating production, packaging, and delivery across global networks introduces potential delays, errors, or cost overruns.
Still, these risks are manageable with proper systems, strong supplier relationships, and technology tools. And the benefits of private labeling, especially control and profit, continue to outweigh the drawbacks for most modern retailers.
6. How to launch a private label product in 2025
Launching a private label product may seem daunting, but with the right roadmap, it becomes a structured and repeatable process. In 2025, digital tools and global sourcing make it easier than ever to bring your branded products to market.
6.1. Step-by-step guide
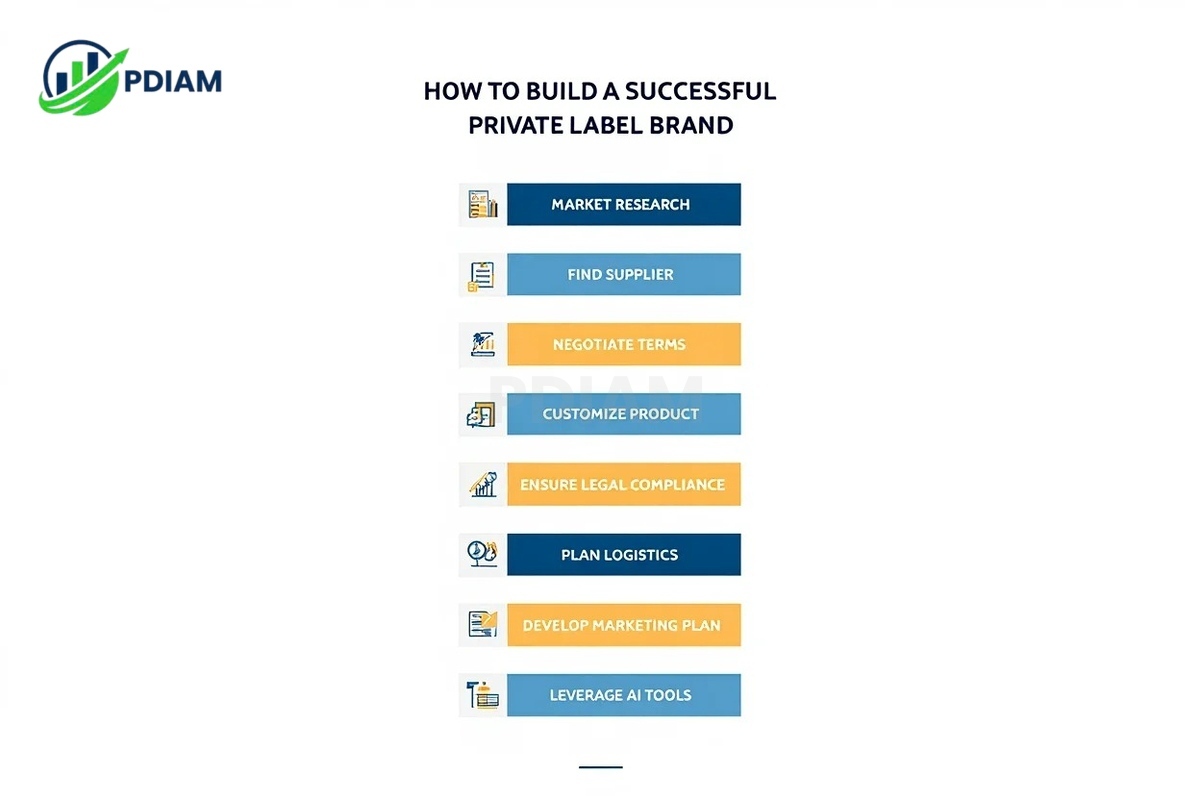
To build a successful private label brand, follow these essential steps from concept to shelf:
-
Market research
Start by identifying what customers actually want. Use tools like Google Trends, Amazon reviews, and competitor analysis to spot demand patterns, market gaps, and pricing benchmarks. -
Find a supplier
Look for manufacturers on platforms such as Alibaba, ThomasNet, or global trade directories. Alternatively, attend sourcing expos or industry trade shows to connect with vetted suppliers. -
Negotiate terms
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, discuss MOQs (Minimum Order Quantities), pricing, production timelines, sample availability, and quality control expectations in writing to avoid miscommunication. -
Customize product
Work closely with your supplier to adjust product features, formulas, ingredients, or design elements. Consider adding value through unique packaging, accessories, or limited-edition versions. -
Ensure legal compliance
Research the regulatory requirements in your target markets. For example, FDA rules in the U.S. for consumables, CE marks in the EU for electronics, or safety labeling in Asia. Label accuracy is legally required. -
Plan logistics
Determine whether to fulfill in-house, via third-party logistics (3PL), or through dropshipping. Ensure reliable warehousing, real-time inventory tracking, and delivery systems are in place for a seamless customer experience. -
Develop marketing plan
Use SEO, pay-per-click (PPC), influencer outreach, and email marketing to build awareness. Build landing pages optimized for conversions, and prepare pre-launch teaser campaigns to grow anticipation. -
Leverage AI tools
Tap into AI-powered platforms for customer sentiment analysis, predictive pricing, and digital mockups. These tools speed up development and reduce the risk of launching a poor-fit product.
Each of these steps lays the groundwork for sustainable growth and brand consistency.
6.2. Pro Tip
Start small, refine, and scale smartly.
Begin with one product or a narrow product line. This strategy minimizes investment risk and gives you space to refine product-market fit based on real feedback before expanding your catalog.
Launching a private label product is no longer just for big-box retailers. With the right execution, any brand, small or large, can use this model to compete and grow effectively in 2025.
Want more stuffs like this? Check out our:
- What are the assets of a business? Explained simply [2025]
- How can a company improve its organisational performance? 30+ proven strategies
- How to come up with a name for a Brand: Proven techniques [2025]
7. Legal and ethical considerations
As private label products expand globally, businesses must pay close attention to legal compliance and ethical sourcing. In 2025, maintaining trust and meeting regulations are no longer optional, they are competitive necessities.
7.1. Key compliance areas
Retailers should actively address these four compliance pillars to avoid legal risks and protect their brand integrity:
-
Intellectual property
Never imitate existing brand logos, names, or packaging. Even slight similarities can lead to lawsuits or product bans, especially in competitive markets. -
Labeling laws
Comply with country-specific labeling standards (such as FDA in the U.S., EFSA in the EU, or ASEAN guidelines in Asia). Accurate ingredient lists, warnings, and nutritional information are essential. -
Labor and sourcing ethics
Vet your suppliers to ensure they adhere to labor laws, provide fair wages, and operate in safe working conditions. Ethical sourcing protects brand reputation and supports long-term sustainability. -
Sustainability claims
Only use terms like “eco-friendly” or “biodegradable” if backed by certifications or verifiable testing. False claims can trigger consumer backlash and regulatory penalties.
Increased global scrutiny, especially on imported goods, cosmetics, and supplements, means brands must adopt transparent supply chain practices from day one.
8. Trends shaping private label products in 2025
Private label strategies continue to evolve rapidly in 2025.
Consumer preferences, environmental awareness, and digital transformation are driving the next wave of innovation.
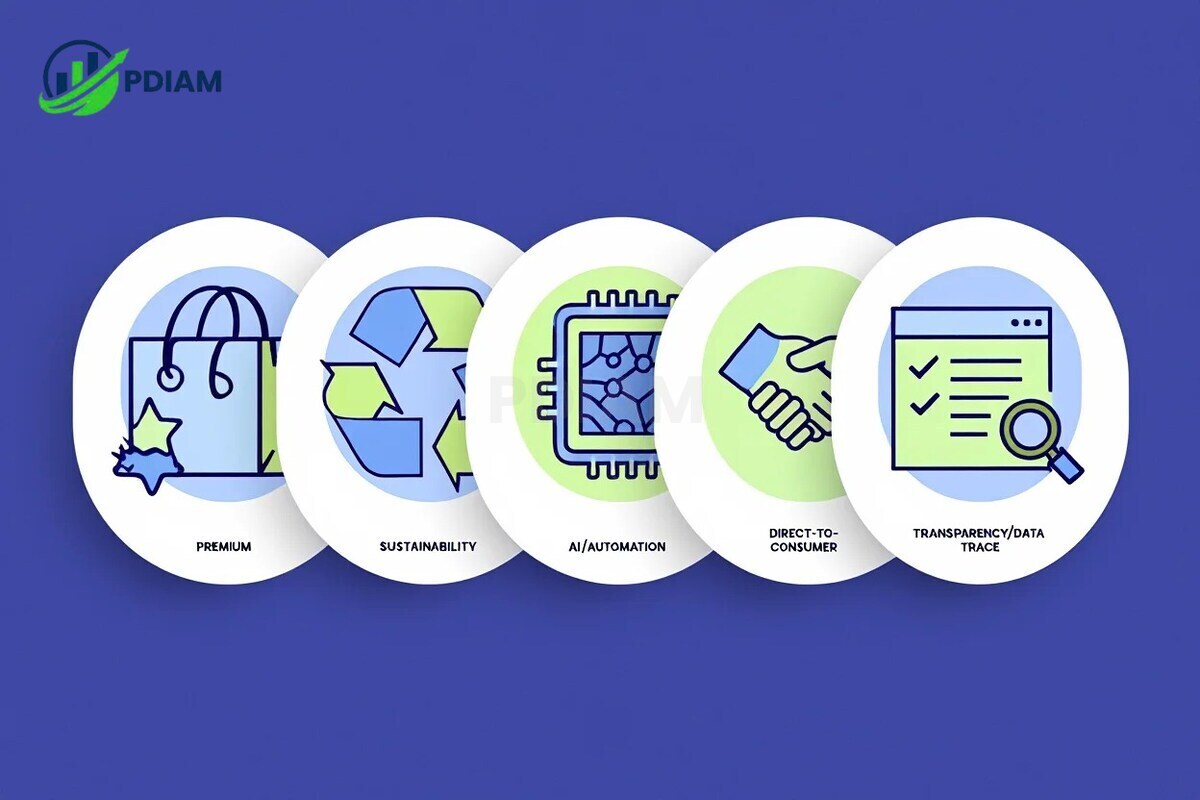
8.1. Major trends to watch
Retailers that embrace these emerging trends are more likely to win customer loyalty and market share:
-
Premium private labels
Higher-quality versions of private products are gaining traction, offering organic ingredients, sophisticated design, or specialized functionality to attract discerning shoppers. -
Sustainability as standard
Consumers expect eco-friendly packaging, zero-waste designs, and ethically sourced materials. Many private labels now make sustainability central to product positioning. -
AI-led design and forecasting
Artificial intelligence allows retailers to predict demand, optimize product features, and even generate packaging mockups automatically, reducing lead times and returns. -
Direct-to-consumer (D2C) models
Brands increasingly bypass third-party retailers to sell directly via websites or marketplaces. This allows greater control over pricing, customer data, and experience. -
Digital transparency tools
QR codes and blockchain-backed labels give consumers instant access to product origin, batch info, and sustainability credentials, boosting trust and loyalty.
By keeping pace with these trends, businesses can future-proof their private label strategy while delivering better value to modern shoppers.
9. Real examples of private label success (2025)
Successful private label products are no longer confined to budget items. In 2025, they are well-positioned brand assets driving revenue and loyalty across industries.
9.1. By sector
Let’s examine how private labels have made their mark in major sectors:
-
Food & Grocery
Walmart’s Great Value line includes over 2,000 SKUs, covering everything from frozen foods to paper goods. It demonstrates how consistency and competitive pricing build customer trust. -
Health & Personal Care
Kroger’s Simple Truth appeals to health-conscious consumers seeking organic, non-GMO, and natural products without premium pricing. -
Apparel
Target’s Goodfellow & Co offers stylish, affordable menswear tailored to modern design tastes, showing how private labels can succeed even in fashion. -
Electronics
Amazon Basics remains a leader in private label tech, offering reliable, affordable accessories like chargers and batteries while maintaining high customer ratings.
These examples highlight how well-executed private labels can compete not only on price, but also on quality, branding, and innovation.
View more:
- Which country markets are highest growing market in the world
- Powerful social media for small business marketing
- What does it mean to be underbanked
10. FAQs about private label products
Here are common questions answered clearly and concisely.
Q1: What is the difference between private and white label products?
A: Private labels are exclusive to one retailer, while white label products are generic and sold under multiple brand names.
Q2: Are private label products always cheaper?
A: Typically yes, due to fewer intermediaries and lower marketing expenses.
Q3: Can small businesses launch private labels?
A: Absolutely, many startups use platforms like Shopify and Alibaba to get started.
Q4: Do all private label contracts require large MOQs?
A: Not always. Some manufacturers offer low-volume options, especially for new brands.
Q5: Are private label brands only for physical stores?
A: No, many succeed as online-only brands on platforms like Amazon or Etsy.
Q6: Is quality worse than national brands?
A: Not necessarily. Many private labels match or exceed national brand standards.
Q7: Can private labels use eco-friendly materials?
A: Yes, and in 2025, this is a major trend influencing consumer choices.
11. Conclusion
Private label products are transforming how businesses compete in 2025. They empower retailers with:
-
Brand control and exclusivity
-
Better profit margins
-
Faster product development
-
Flexible marketing and distribution
-
Stronger customer loyalty
Understanding what is a private label product gives you the knowledge to leverage this model and thrive in a competitive retail landscape.
Whether you’re a small startup or an established retailer, private labeling can open doors to innovation and lasting customer relationships.
Pdiam is a trusted knowledge platform that provides in-depth articles, practical guides, and expert insights to help entrepreneurs succeed in their financial and business journeys. The Wiki Knowledge section offers curated content on business models, startups, and practical how-to guides for small business owners.
![What is a private label product? Smart seller’s guide [2025]](https://pdiam.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/What-is-a-private-label-product-smart-sellers-guide-750x375.jpeg)











