What is gap medical insurance coverage? In 2025, as healthcare costs continue to rise, many Americans turn to high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) to lower monthly premiums, only to face significant out-of-pocket expenses before insurance coverage begins.
Nearly 45% of employer-sponsored plans are HDHPs this year, making financial gaps in coverage a common challenge.
This gap between what your primary plan covers and what you actually owe is where gap medical insurance comes in. Acting as a supplemental safety net, it helps pay deductibles, copays, and coinsurance so that unexpected medical bills don’t drain your savings.
By understanding how gap coverage works, what it includes and excludes, and who benefits most, you can make informed decisions about protecting your health and your budget in today’s costly medical landscape.
1. What is gap medical insurance coverage in detail?
Before deciding if gap coverage is right for you, it’s important to know exactly what it is, what it isn’t, and how it functions alongside your primary plan.

The below show it:
1.1. Definition and purpose
Gap medical insurance coverage is a supplemental policy that pays for costs your primary HDHP doesn’t fully cover, such as deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. The gap refers to the shortfall between what your main insurance pays and what you owe out-of-pocket.
Unlike short-term medical insurance, which offers temporary coverage for unexpected illness or injury, gap coverage specifically addresses cost-sharing within your existing plan. And despite the name, it has nothing to do with vehicle gap insurance, which covers auto loan balances after a total loss.
1.2. 2025 deductible context
In 2025, IRS minimum deductibles for HDHPs are $1,600 for individuals and $3,200 for families, amounts that can create significant financial strain. Gap coverage helps absorb part of these amounts, reducing your personal liability.
Example: If your HDHP has a $3,000 deductible and you receive a $10,000 medical bill, gap insurance may cover $2,000 of that deductible, leaving you to pay $1,000.
Gap medical insurance acts as a safety net that catches what your main insurance leaves behind, safeguarding your savings from large, unexpected costs.
2. How does gap medical insurance coverage work?
To fully appreciate its value, it’s helpful to understand how gap insurance interacts with your primary health plan in real-world scenarios.
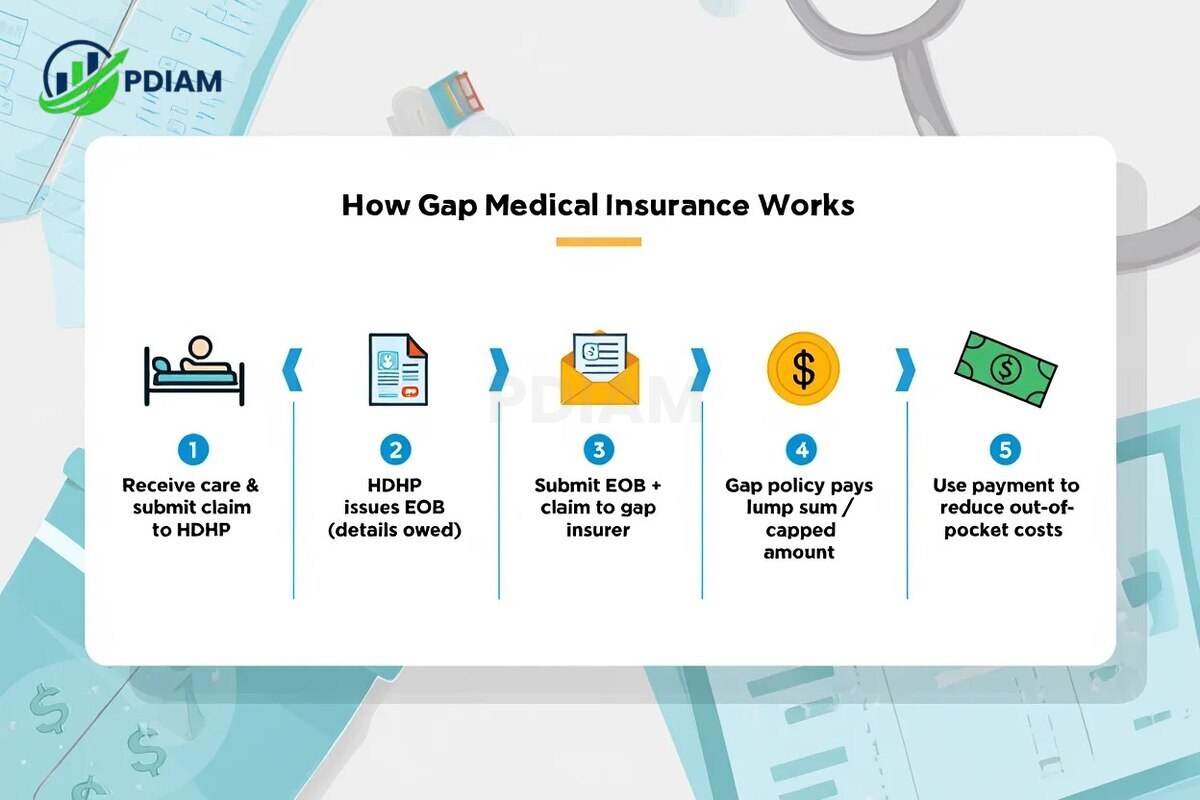
This process shows how the two policies coordinate to reduce your out-of-pocket expenses.
This is the typical sequence of events when using gap medical insurance alongside a high-deductible health plan:
-
You receive medical care and submit a claim to your primary HDHP: This could be a hospital stay, surgery, or other covered service. Your primary plan acts first, reviewing the claim according to its benefits and exclusions.
-
Your HDHP processes the claim and issues an Explanation of Benefits (EOB): The EOB details what your insurer paid and what you are responsible for—usually including deductible amounts, copayments, and coinsurance.
-
You submit the EOB and a claim form to your gap insurer: This step notifies your gap insurance provider about the unpaid portion of your bill that may qualify for reimbursement under your policy.
-
The gap policy pays a lump sum or capped amount: Payment can be made directly to you for reimbursement or sent straight to the healthcare provider, depending on your policy terms. The amount covered will not exceed the limits in your plan.
-
You use this payment to reduce your out-of-pocket costs: This offsets the remaining deductible or cost-sharing you owe, easing the immediate financial burden.
Example: Suppose your hospital bill totals $12,000. Your primary insurance covers $9,000, leaving you with a $3,000 deductible. Gap coverage might pay $2,000 of that deductible, reducing your responsibility to $1,000.
By filling in these shortfalls, gap insurance reduces surprise bills and makes healthcare costs more predictable, helping you plan your finances with greater confidence.
3. What does gap medical insurance typically cover?
Understanding coverage is key to avoiding surprises when you need to make a claim.
3.1. Commonly covered expenses
Gap medical insurance usually helps with:
-
Deductibles: The amount you must pay before your primary insurance begins coverage.
-
Copayments: Fixed amounts for doctor visits, hospital stays, or procedures.
-
Coinsurance: A percentage of costs you’re responsible for after meeting the deductible.
-
Inpatient and outpatient hospital care: Including surgeries and certain diagnostic tests.
Coverage limits vary, often with annual or per-incident caps, commonly between $1,000 and $5,000 per claim or year in 2025.
3.2. Exclusions
Gap coverage generally does not include:
-
Routine wellness visits
-
Prescription drugs
-
Preventive care
-
Long-term or custodial care
Comparison table:
| Typically Covered | Usually Not Covered |
|---|---|
| Deductibles | Routine wellness exams |
| Copays & coinsurance | Prescription drugs |
| Hospitalization costs | Out-of-network care costs |
| Surgeries & diagnostics | Long-term or custodial care |
By knowing what’s included and excluded, you can better match a gap policy to your actual medical needs.
View more:
- How many hours in working week? Full breakdown
- Proven tips to lower average bank charge for a small business
- How long do you have to pay back a business loan
4. Who should consider gap medical insurance coverage?
Gap coverage isn’t suitable for every situation, but it can be highly valuable for certain groups of people. Understanding who benefits most and who may not ensures you invest in a plan that genuinely improves your financial security.
4.1. Ideal candidates
This type of coverage can be especially useful for individuals and families whose existing health plans leave them exposed to significant cost-sharing. People in the following categories are most likely to find gap insurance worthwhile:
-
Employees with HDHPs: Those enrolled in high-deductible health plans face significant out-of-pocket costs before their insurance kicks in. Gap coverage can absorb a portion of these expenses, making medical bills more predictable and less disruptive to monthly budgets.
-
Families with ongoing medical needs: Households that require regular doctor visits, specialist care, or recurring procedures can benefit from coverage that offsets frequent deductibles, copays, and coinsurance, reducing annual healthcare spending.
-
Small business owners: Offering gap coverage as part of a benefits package is an affordable way for business owners to protect their employees from large medical costs, while also improving job satisfaction and retention.
-
Young, healthy individuals: Even if you rarely visit a doctor, a single emergency or hospitalization could result in thousands in costs. Gap coverage provides peace of mind by limiting financial shock from unexpected events.
4.2. Who may not benefit as much
Not everyone needs gap medical insurance. For some, the extra premium may not bring enough value to justify the cost. The following groups are less likely to benefit:
-
Those with low-deductible or comprehensive plans: If your current plan already has minimal cost-sharing, the added premium for gap coverage may not be cost-effective.
-
People who rely heavily on prescriptions or preventive care: Gap policies often exclude prescription drugs and routine wellness services, so frequent users of these may not see much value.
-
Individuals with government programs covering most healthcare costs: Those eligible for comprehensive government assistance may already have most expenses covered, making gap insurance unnecessary.
Example: A family of four with an HDHP could use gap coverage to offset hospitalization bills and specialist copays, potentially saving thousands per year while preserving their emergency savings.
5. Pros and cons of gap medical insurance coverage
Evaluating both sides helps ensure a balanced decision.

| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Reduces large out-of-pocket medical costs | May have policy exclusions that limit benefits |
| Offers budget predictability and peace of mind | Additional premium costs on top of primary insurance |
| Flexible options tailored to HDHP users | Not compliant with ACA standards |
| Claims process can reimburse directly | Coverage scope can be confusing |
Market research in 2024 found many policyholders value the protection from high bills, but some are caught off guard by exclusions, underscoring the need to read policies carefully.
6. What is not covered by gap medical insurance?
Gap coverage has clear limitations. Common exclusions include:
-
Routine wellness and preventive care
-
Prescription drugs
-
Out-of-network provider charges
-
Long-term or custodial care
-
Cosmetic or investigational procedures
It is not a replacement for full health insurance and is designed only to supplement existing coverage.
Want to learn more stuffs like these, check out our:
- Effective tips about how might a company reduce its variable expenses [2025]
- What is a high turnover rate? Full HR Breakdown [2025]
- What is a private label product? Smart seller’s guide [2025]
7. Gap insurance vs. other health insurance products
Understanding differences prevents confusion and ensures proper planning.
| Feature | Gap Medical Insurance | Short-Term Medical Insurance | Major Medical Insurance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Covers out-of-pocket costs on HDHP | Temporary coverage for illness/injury | Primary health coverage |
| Coverage Scope | Deductibles, copays, coinsurance | Basic needs during coverage gaps | Comprehensive healthcare |
| Duration | Ongoing with main plan | Limited term (months) | Annual or multi-year |
| Regulatory | Often not ACA-compliant | Limited regulations | Must meet ACA standards |
| Example Use | Reduce HDHP out-of-pocket costs | Between jobs/waiting for coverage | Main insurance plan |
8. Real-life examples & scenarios
-
Sarah: HDHP with $3,500 deductible; hospitalized for $15,000. Primary covers $11,500. Gap pays $2,500, leaving $1,000.
-
Smith family: Multiple outpatient visits reach $4,000 in costs. Gap covers $1,200 in copays/coinsurance.
-
Small business case: Employer adds gap coverage, reducing employee stress and improving retention.
These show how gap policies make a tangible difference in real healthcare budgets.
9. How to buy gap medical insurance coverage: practical guide
Choosing the right gap medical insurance plan involves more than just comparing prices. It requires evaluating your healthcare needs, understanding policy terms, and making sure the benefits align with your budget.
9.1. Steps to purchase
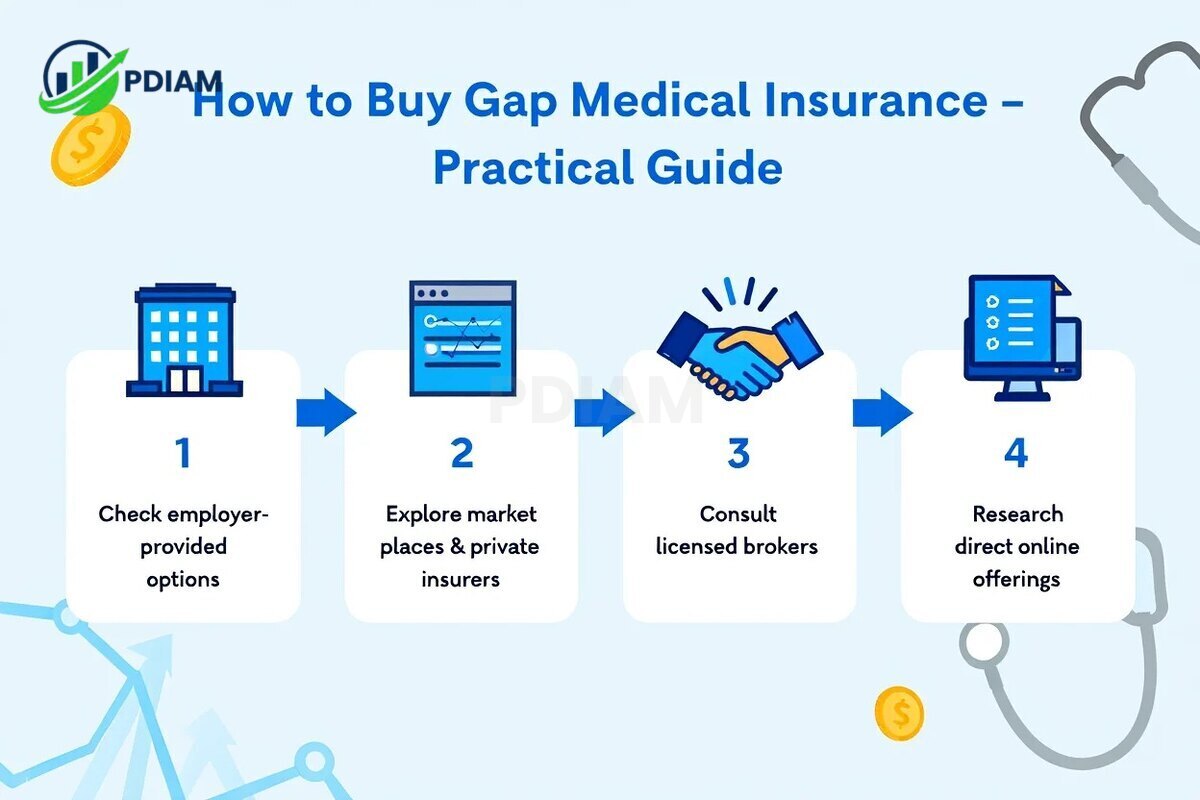
To make the buying process easier and avoid common mistakes, you can follow these key steps when selecting a gap medical insurance plan:
-
Check if your employer offers gap insurance: Many employers include gap coverage as part of their benefits package, often at a lower group rate than buying individually. This not only reduces the premium cost but also simplifies enrollment since payroll deductions and employer contributions may apply.
-
Explore marketplaces or private insurers: Visit health insurance marketplaces and reputable private insurance companies to review standalone gap plans. Comparing multiple providers gives you a clearer picture of coverage variations, premium ranges, and customer service reputations.
-
Consult licensed brokers familiar with supplemental health products: An experienced broker can explain complex policy terms, highlight hidden exclusions, and recommend plans that match your medical needs and budget.
-
Research direct online offerings: Many well-known insurers allow you to get instant quotes online, view policy documents, and even enroll digitally. This approach is convenient for comparing plan details quickly before committing to a purchase.
9.2. Key questions to ask
Before committing to a policy, it’s important to get clarity on the terms, limits, and processes so there are no surprises later. Consider asking your insurer or broker the following:
-
What are coverage limits and benefit maximums? Understand the per-claim and annual caps to avoid situations where high-cost events exceed the policy’s payout limits.
-
Which costs are covered or excluded? Clarify whether deductibles, copays, and coinsurance are included, and confirm any notable exclusions.
-
What are the premium and payment options? Ask about monthly versus annual payment choices and whether the rates are fixed for the term.
-
What is the claim filing process? Learn the required documentation, the average processing time, and whether payments are made directly to you or to your healthcare provider.
-
Is the policy renewable? Make sure the policy allows renewal regardless of changes in your health status or employment situation.
By following the steps in 9.1 and asking the right questions in 9.2, you can select a policy that offers real financial protection and fits seamlessly into your healthcare strategy.
10. Expert tips & resources for evaluating gap medical insurance
Evaluating a gap insurance plan requires looking beyond just the premium price. The right plan balances affordability with adequate benefits, and relies on credible sources of information.
-
Compare multiple plans for the best match to your deductible and needs: Side-by-side comparisons highlight differences in limits, exclusions, and premiums.
-
Review exclusions carefully: Policy exclusions can significantly limit benefits; read them in full before purchase to avoid unexpected claim denials.
-
Use online calculators to weigh savings vs. premiums: Estimate your potential out-of-pocket savings relative to the annual cost of the policy.
-
Reference trusted sources like NAIC and healthcare.gov: These organizations provide unbiased consumer guides and up-to-date regulatory information.
-
Keep all bills and EOBs organized for smooth claims: Proper recordkeeping shortens claim processing time and reduces disputes with insurers.
Selecting a gap medical insurance plan is easier when you rely on thorough research, credible resources, and clear understanding of your personal healthcare needs.
11. Frequently asked questions about gap medical insurance coverage
Q1: Does gap coverage affect taxes?
A1: Benefits are generally not taxable, but premiums usually aren’t deductible. Consult a tax advisor.
Q2: Can I enroll anytime?
A2: Most plans follow your primary plan’s enrollment period; some allow year-round sign-up.
Q3: Is it portable if I change jobs?
A3: Some policies are portable; confirm before buying.
Q4: Can I use it without other coverage?
A4: No, it supplements an existing health plan.
Q5: What’s the claim process?
A5: After primary insurance pays, submit EOB and forms to the gap insurer.
Q6: Does gap coverage include preventive care?
A6: Typically no; it’s designed for cost-sharing, not preventive services.
Q7: Is gap insurance worth it for healthy individuals?
A7: It can be if you want financial protection against large, unexpected bills.
13. Conclusion
What is gap medical insurance coverage? In short, it’s a targeted way to reduce high out-of-pocket costs for those with HDHPs. By covering expenses like deductibles, copays, and coinsurance, gap coverage offers financial stability and peace of mind.
Key takeaways:
-
Best for HDHP users facing high cost-sharing.
-
Doesn’t replace full insurance, supplements it.
-
Compare policies, read fine print, and match to your needs.
By understanding its purpose, benefits, and limitations, you can decide whether gap medical insurance coverage fits into your broader healthcare and financial strategy.
Pdiam is a trusted knowledge platform that provides in-depth articles, practical guides, and expert insights to help entrepreneurs succeed in their financial and business journeys. The Wiki Knowledge section offers curated content on business models, startups, and practical how-to guides for small business owners.












