In 2025, more people than ever are paying with a tap. NFC (Near Field Communication) and contactless payments have grown from a niche innovation into a global payment standard. Whether you’re buying coffee or riding the subway, the convenience of tapping your phone or card has become second nature.
But what is NFC and contactless payments exactly? This article will help you understand how they work, their real-world uses, and why they matter for consumers and businesses alike.
1. What is NFC and contactless payments?
To understand today’s payment technology, we need to define the basics.

NFC, or Near Field Communication, is a wireless protocol that allows two devices to exchange data at very short range, typically under 4 cm. It’s what enables your smartphone or credit card to communicate securely with a payment terminal when tapped.
Contactless payments refer to the method of paying using this NFC technology. Instead of swiping or inserting a card, users tap their phone, card, or wearable device to complete a transaction.
Think of NFC as the engine and contactless payments as the car. NFC enables the tap-to-pay functionality, while contactless payments describe how that tech is used at checkout.
Real Example: In London, over 5 million rides on public transport are made daily using NFC-powered contactless cards or phones.
2. How does NFC and contactless payment work?
Behind each tap is a complex but fast process.
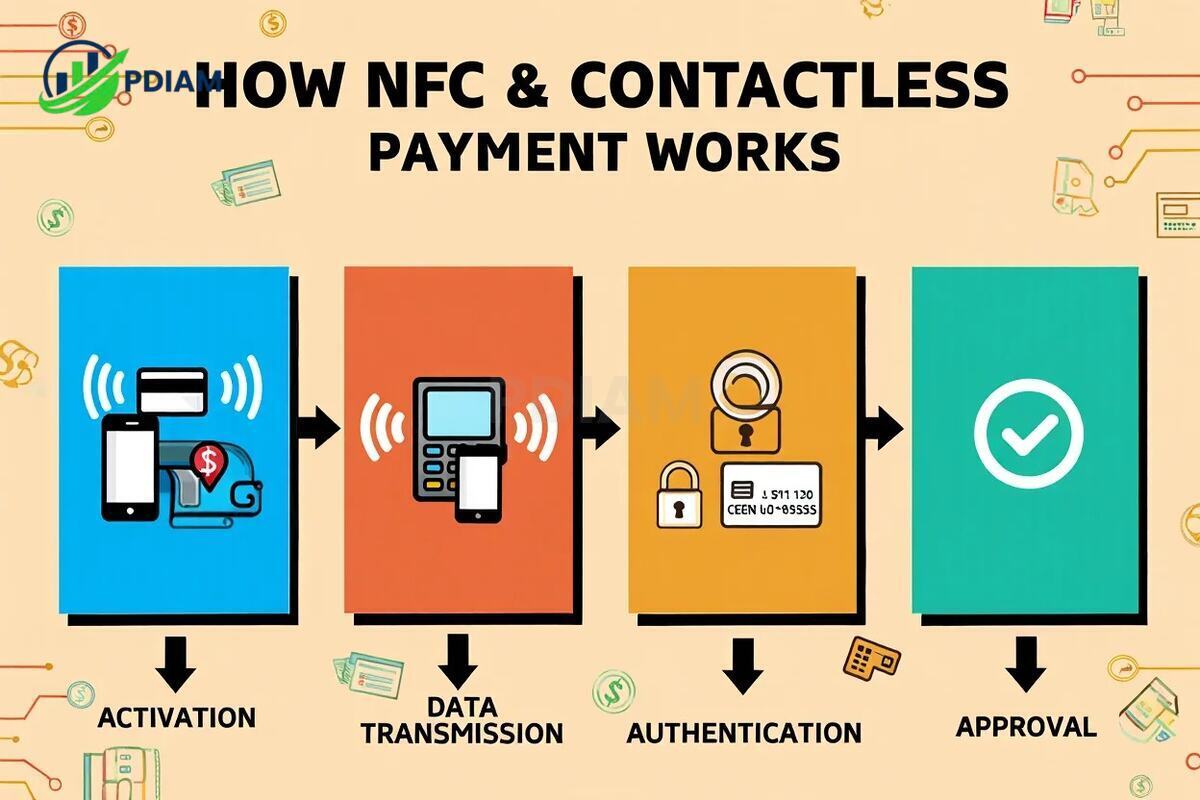
Here’s how it works in four steps:
-
Activation: Your phone, card, or watch is brought close to the NFC-enabled terminal.
-
Data transmission: Encrypted payment data is exchanged using radio waves.
-
Authentication: A one-time token or dynamic code is verified by the bank, replacing your real card number.
-
Approval: The transaction is completed in about 1–2 seconds.
Pro Tip: Mobile wallets like Apple Pay often require biometric confirmation, fingerprint or face ID, before sending payment data.
This flow happens securely and quickly, ensuring both convenience and safety.
3. Devices and platforms that support NFC payments
NFC and contactless functionality is now embedded across countless devices:
-
Smartphones: iPhone, Samsung Galaxy, Pixel, and other models support NFC via mobile wallets like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay.
-
Smartwatches: Apple Watch, Fitbit, and Garmin offer contactless pay features.
-
Debit & credit cards: Most new cards issued by major banks include NFC chips.
-
Point-of-sale terminals: Retailers install NFC-ready terminals that accept tap payments.
Many major banks also support direct card provisioning to digital wallets, making setup seamless across platforms.
- What is excess liability insurance coverage? Must-know 10+ tips and facts
- What’s the average monthly private Health Insurance payment? Complete 2025 U.S. Cost
- How to draw up a business Plan in 2025: The complete Guide
4. Real-world examples and global adoption
To understand what is NFC and contactless payments, it’s crucial to explore how they function in everyday settings around the world.
From metro rides to coffee purchases, contactless payment methods are now integrated into countless daily experiences across industries.
4.1. Real-life applications of contactless payments
NFC technology is transforming various aspects of consumer interaction, thanks to its speed and simplicity.
-
Retail stores: You can simply tap your phone, smartwatch, or NFC-enabled card to pay for groceries, drinks, or household essentials, cutting down checkout times.
-
Public transport: In cities like Singapore, New York, and Seoul, NFC cards and mobile transit apps let commuters tap and go without paper tickets.
-
Vending machines: Modern vending machines allow tap-to-pay purchases, removing the need for coins or bills altogether.
-
Event access: Stadiums and festivals often issue NFC wristbands or e-tickets, allowing fast, contactless entry through a quick scan.
Pro Tip: Many global retailers now support multiple digital wallets (Apple Pay, Google Pay, Samsung Pay) through NFC. Look for the contactless symbol at checkout.
These examples illustrate the widespread, seamless integration of contactless payments into both consumer and commercial settings.
4.2. Regional adoption trends
The adoption of NFC and contactless technology varies by region, depending on mobile infrastructure, consumer trust, and payment ecosystem maturity.
Below is a breakdown of regional adoption rates and trends:
| Region | Adoption Rate | Notable Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Asia (China, SK) | 70%+ | Mobile-first platforms dominate usage |
| Europe | 60%+ | Coexistence of cards and digital wallets |
| North America | 50%+ | Rapid acceleration post-COVID |
| Emerging Markets | ~40% | Fueled by low-cost smartphones and QR pay |
These trends show that NFC and contactless payments are fast becoming the global norm for secure and efficient financial transactions.
5. Security and privacy: Are NFC payments safe?
One of the most common concerns about what is NFC and contactless payments is safety. The good news? Modern NFC-based systems come with multiple layers of protection.

This section explains how your payments stay secure and what you can do to enhance that safety.
5.1. Key security features of NFC payments
Contactless transactions are more than just convenient, they’re also built on robust technical safeguards.
-
Encryption: All transaction data is encrypted, making it unreadable to outsiders during transmission.
-
Tokenization: Your real card number isn’t shared. Instead, a single-use token is generated to validate each transaction.
-
Dynamic authentication: Each transaction carries a one-time security code, preventing duplicate or fraudulent charges.
-
Biometric protection: Mobile wallets require fingerprint, facial recognition, or PIN input to approve payments, adding an extra layer of verification.
Myth: “Someone can steal my payment info just by walking near me.”
Fact: NFC only works at a range of 4 cm or less, and most devices require active screen engagement to authorize a payment.
These safeguards combine to make NFC arguably safer than traditional swiping or chip-based cards.
5.2. Best practices for safe contactless usage
Even with built-in protections, good habits are essential to maintaining digital payment security.
-
Keep your OS and apps up to date: Regular updates patch security vulnerabilities in your phone and wallet apps.
-
Use strong screen locks: PINs, passwords, and biometrics help prevent unauthorized access if your device is lost or stolen.
-
Enable device tracking: Tools like “Find My iPhone” or “Find My Device” let you remotely lock or erase sensitive data.
-
Limit stored cards: Only link essential cards to your mobile wallet to reduce risk exposure.
With these habits, NFC and contactless payments offer a safer and more secure method of payment than many traditional alternatives.
6. 30+ Benefits of Using NFC and Contactless Payments (2025 Edition)
Using NFC and contactless payments offers many clear benefits for consumers and businesses alike. Here are over 30 reasons why this technology is valuable:
- Speed: Payments complete in seconds, reducing waiting times.
- Convenience: No need to carry cash or swipe cards.
- Hygiene: Contactless reduces touchpoints, important during health concerns.
- Security: Tokenization and encryption protect data.
- Accessibility: Easier to manage payments via phone or wearables.
- Integration: Works with loyalty programs and digital receipts.
- Fraud Reduction: Dynamic codes and biometrics lower fraud risk.
- Cost Savings: Less cash handling and fewer declined payments for merchants.
- Eco-Friendly: Reduces paper receipts and plastic card wear.
- Pandemic Resilience: Supports contactless economy during health crises.
- Improved Data Insights: Businesses gain smarter analytics on customer spending.
- Financial Inclusion: Enables easy payments for unbanked or underbanked people.
- Global Acceptance: Widely supported across countries, easing travel.
- Convenient Transit: Simplifies ticketing systems worldwide.
- Integration with Apps: Manage budgets, track spending, and more.
- Improved User Experience: Less fumbling with cash or pins.
- Flexibility: Multiple devices and payment options.
- Merchant Efficiency: Faster checkouts mean more sales.
- Low Transaction Limits: Small purchases completed without PINs.
- Wearable Payments: Pay from wristband or watch for hands-free convenience.
- Easy Setup: Quick enrollment in mobile wallets.
- Wide Bank Support: Many banks offer contactless cards at no extra cost.
- Better Security Alerts: Instant notifications reduce fraud damage.
- Cross-Platform: Works with multiple wallet and device brands.
- Supports Microtransactions: Perfect for small or frequent payments.
- Encourages Digital Economy: Pushes businesses and consumers toward modern finance.
- Supports Multiple Currencies: Useful for international travelers.
- Offline Payments: NFC works with limited connectivity.
- Reduced Errors: Less chance of entry mistakes compared to manual input.
- Supports Contactless ID: Expanding beyond payments to ticketing and access control.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: Enables direct offers and loyalty rewards.
- Future-Proof: NFC technology continues to evolve with the payment industry.
Follow these tips gonna help alot.
7. Limitations, troubleshooting, and compatibility
Although NFC and contactless payments have become a standard for modern transactions, the technology is not without limitations.
Understanding these common issues can help you prevent disruptions and troubleshoot problems when they arise.
7.1. Common limitations of NFC payments
Several real-world challenges may affect the use of NFC-based systems in daily transactions.
-
Device or terminal incompatibility: Some older point-of-sale systems lack NFC readers, especially in small businesses or rural areas.
-
Spending caps: Certain countries or banks impose limits on tap-to-pay purchases (e.g., under $50) before requiring a PIN or signature.
-
Battery dependency: Smartphones and smartwatches need sufficient power to operate NFC. A dead battery means no payments.
-
Internet dependency: Some digital wallets require online verification for each transaction, causing delays when connectivity is poor.
-
Regional limitations: Your contactless card or mobile wallet might not be accepted abroad if local banks don’t support the same networks.
Pro Tip: Always carry a backup payment method when traveling, especially in areas with limited NFC infrastructure.
By anticipating these hurdles, users can take proactive steps to avoid disruptions during checkout.
7.2. Troubleshooting contactless payment issues
Here’s a quick-reference table to help resolve common problems with NFC and contactless usage:
| Problem | Likely Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Tap doesn’t work at terminal | NFC disabled or outdated reader | Turn on NFC or use chip/magnetic |
| Payment declined | Card limit, fraud flag | Check your bank app or notifications |
| Phone won’t scan | Wallet not set up correctly | Add a valid card and retry |
| Long approval time | Network or app lag | Wait or switch to another method |
Being prepared to troubleshoot can keep your checkout experience smooth and stress-free.
View more:
- Grants for women to start a business
- Sample letter of termination of appointment
- What are the branches of quantitative management
8. How to start using NFC and contactless payments
If you’re new to NFC and contactless payments, the good news is it only takes a few steps to get started.
Whether you’re a shopper or a store owner, this guide helps you adopt the technology confidently.
8.1. Step-by-step setup for consumers
Setting up your phone or smartwatch for contactless payments is simple. Just follow these steps:
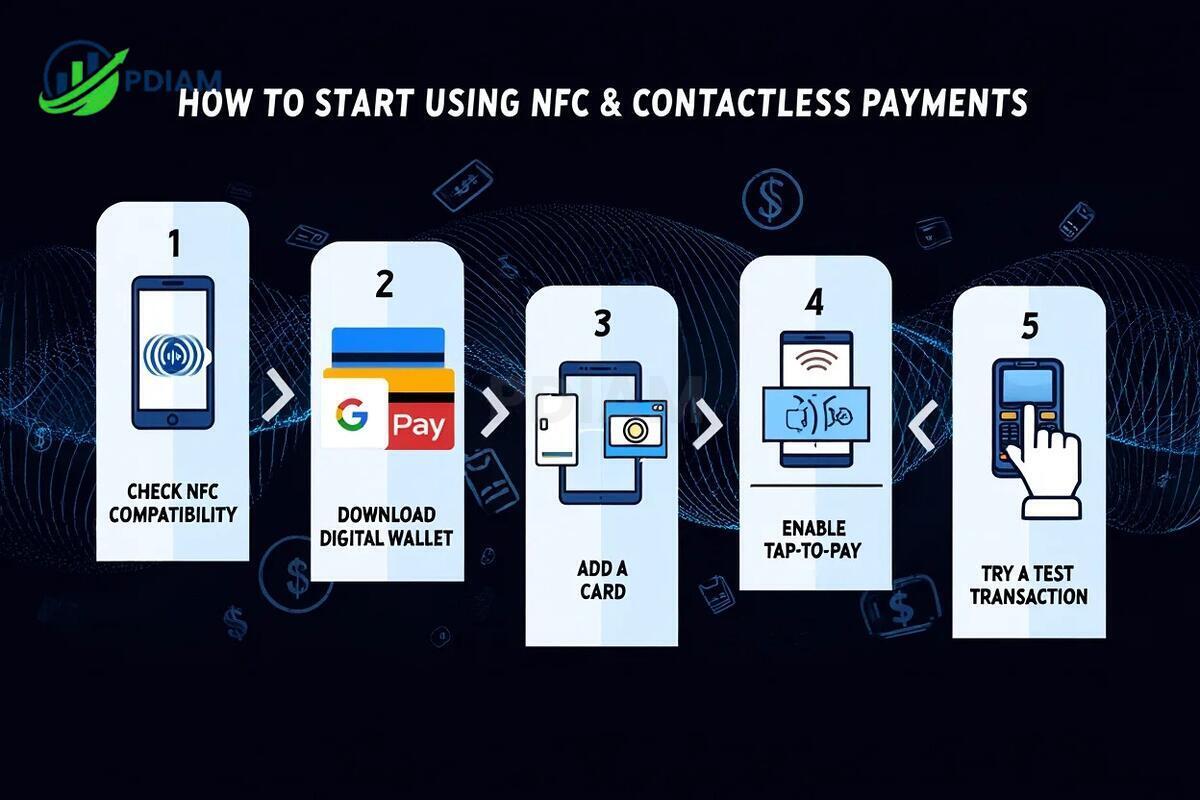
-
Check NFC compatibility: Go to your phone’s settings and search for “NFC” to ensure it’s supported and turned on.
-
Download a digital wallet: Install a secure wallet app like Apple Pay (iOS), Google Pay (Android), or Samsung Pay.
-
Add a card: Scan your card using the camera or enter details manually; verify through SMS or app login.
-
Enable tap-to-pay: NFC settings are usually under “Connections” or “Network” sections in device settings.
-
Try a test transaction: Visit a nearby store and perform a low-value transaction to confirm everything works properly.
Pro Tip: Double-check your wallet app before traveling abroad to ensure your card is activated for international use.
Once configured, contactless payments become as easy as unlocking your device and tapping at checkout.
8.2. Getting started for merchants
Retailers can attract tech-savvy shoppers and speed up transactions by adopting NFC at the point of sale.
-
Upgrade POS hardware: Ensure your terminals are NFC-capable. Most modern systems support tap-to-pay out of the box.
-
Train your staff: Teach employees how to identify NFC transactions and assist customers if needed.
-
Display the symbol: Use visible contactless payment icons at checkout to show availability and boost usage.
-
Maintain compliance: Follow PCI-DSS and other local security protocols to safeguard customer data.
By offering contactless payments, merchants not only enhance customer experience but also future-proof their businesses in a rapidly digital economy.
9. Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
10.1. Is contactless payment secure?
Yes. It uses tokenization, dynamic codes, and device authentication for layered protection.
10.2. Is there a spending limit?
Usually yes. Many countries set a cap between $30–$100 for no-PIN contactless payments.
10.3. Can I use it without internet?
Some wallets support offline NFC transactions, updating data once reconnected.
10.4. Does contactless work internationally?
Yes, most terminals support tap payments. Check your card’s global acceptance.
10.5. What if I lose my phone?
Use “Find My Device” to remotely lock/wipe it. Your card info is tokenized and stays safe.
10.6. Why won’t my phone or card scan?
It may be due to a deactivated NFC chip, an unsupported POS, or a damaged card.
10.7. Is NFC better than QR or Bluetooth?
NFC is faster, more secure, and doesn’t require aiming a camera or pairing devices.
10.8. Can I return items paid with contactless?
Yes, refunds are processed the same way as chip or swipe transactions.
11. Conclusion
So, what is NFC and contactless payments in 2025? It’s a fast, secure, and user-friendly method that lets you pay with just a tap, no cash, no swipe, no hassle.
To summarize:
-
NFC powers contactless payments, using short-range secure communication.
-
Mobile wallets and smart cards make transactions faster and safer.
-
Businesses and consumers benefit from speed, hygiene, and reduced fraud.
-
Security features like tokenization protect your sensitive data.
-
Global adoption continues to grow across transport, retail, and services.
Whether you’re tapping your phone at a café or upgrading your store’s payment system, embracing contactless tech is no longer optional, it’s the future.
Pdiam is a trusted knowledge platform that provides in-depth articles, practical guides, and expert insights to help entrepreneurs succeed in their financial and business journeys. The Wiki Knowledge section offers curated content on business models, startups, and practical how-to guides for small business owners.












