What is push and pull marketing, and why does it matter today? These two fundamental strategies help businesses reach customers and drive sales in different ways. Push marketing sends your message directly to potential buyers, aiming for immediate action. Pull marketing, on the other hand, draws customers in by building brand interest and loyalty over time.
Understanding both approaches is essential in today’s diverse marketing landscape, where companies blend digital tools and traditional channels to stay competitive. This guide explores the key elements of each strategy, offers comparison frameworks, and provides practical advice to help you choose the right mix.
1. What is push marketing? (Definition, tactics & examples)
Push marketing is a proactive approach where businesses promote products directly to customers through various channels, aiming to “push” the product toward them.

It typically involves outreach rather than waiting for customer interest to develop organically.
1.1. Key characteristics of push marketing
Push marketing is known for its immediacy and broad reach. Below are the primary traits:
-
Proactive and seller-initiated: The business starts the conversation by reaching out to potential customers.
-
Seeks immediate sales or awareness: Often used in campaigns tied to product launches or time-sensitive offers.
-
Appeals to broad audiences: Messaging is designed to reach the masses rather than targeting individuals.
-
Effective for urgency-based campaigns: Helps quickly move inventory or boost short-term performance.
A real-world example is a car dealership promoting a limited-time discount with billboards and cold calls.
1.2. Common push marketing channels & tactics
Push marketing utilizes both offline and online methods to gain immediate visibility:
-
TV and radio ads: Broadcast-wide messages to gain mass attention.
-
Direct mail: Flyers or catalogs sent directly to consumers.
-
Sales calls: Phone outreach targeting leads, especially in B2B.
-
Point-of-sale promotions: Displays or discounts placed in retail environments.
-
Trade shows: Presentations and booths that engage potential partners or buyers.
-
Digital push tactics: Retargeting ads, SMS blasts, and pop-ups encouraging action.
For example, FMCG brands often use in-store promotions at peak shopping hours to trigger fast sales.
1.3. When to use push marketing
Push marketing is ideal for:
-
Launching new products or services.
-
Driving quick traffic to physical or digital stores.
-
Encouraging bulk sales or clearing inventory.
-
Promoting short-term campaigns like flash sales or holiday offers.
Companies like publishers and electronics retailers often rely on push tactics for fast turnover.
1.4. Real-life examples of push marketing
-
Coca-Cola uses eye-catching displays at supermarkets to push impulse purchases.
-
SaaS companies may send cold emails promoting free trials to targeted B2B leads.
-
Retailers promote products with large in-store stands to attract walk-in buyers.
These examples highlight push marketing’s strength in driving immediate visibility and transactions.
2. What is pull marketing? (Definition, tactics & examples)
Pull marketing is a strategy focused on attracting customers who actively seek out your product. It builds brand value and awareness, encouraging demand without direct outreach.
2.1. Key characteristics of pull marketing
Pull strategies aim for sustained growth by nurturing trust and relevance:
-
Customer-initiated: Interest originates from the buyer, not the brand.
-
Focuses on long-term branding: Encourages loyalty and repeated engagement.
-
Highly targeted: Content aligns with specific customer pain points or interests.
-
Trust-driven and gradual: Takes time to develop but builds strong customer relationships.
For instance, influencer campaigns are pull tactics that create authentic demand via social proof.
2.2. Common pull marketing channels & tactics
Pull marketing typically centers on organic and inbound methods:
-
SEO and content marketing: Articles, videos, and resources that attract visitors.
-
Social media engagement: Direct interaction with users and shared stories.
-
Influencer partnerships: Trusted voices promote the product subtly.
-
Email newsletters and webinars: Value-added content builds long-term interest.
-
PR and storytelling: Consistent narratives shape public perception.
Netflix’s investment in original content and Glossier’s focus on community engagement are prime pull examples.
2.3. When to use pull marketing
Pull marketing works best for:
-
Products requiring research or consideration (e.g., software, automobiles).
-
Long-term brand building and customer lifetime value.
-
Niche markets with informed, intentional buyers.
Use cases include:
-
Luxury brands focusing on loyalty and emotional appeal.
-
B2B SaaS companies leveraging inbound strategies for qualified leads.
-
Tech startups providing blogs, demos, and educational material.
2.4. Real-life examples of pull marketing
-
Apple relies on anticipation and organic buzz for new releases.
-
HubSpot draws leads via inbound blog content and free tools.
-
Glossier builds a devoted community through user-driven content and direct engagement.
These brands show how pull marketing fosters strong brand equity over time.
View more:
- How to run a background check on yourself for free in 2025
- Best money management apps for iPhone: Complete guide in 2025
- Definitive guide: Is net income and net profit the same? [2025]
3. What is push and pull marketing: Key differences explained
Understanding the difference between push and pull marketing is key to selecting the right strategy at the right time.
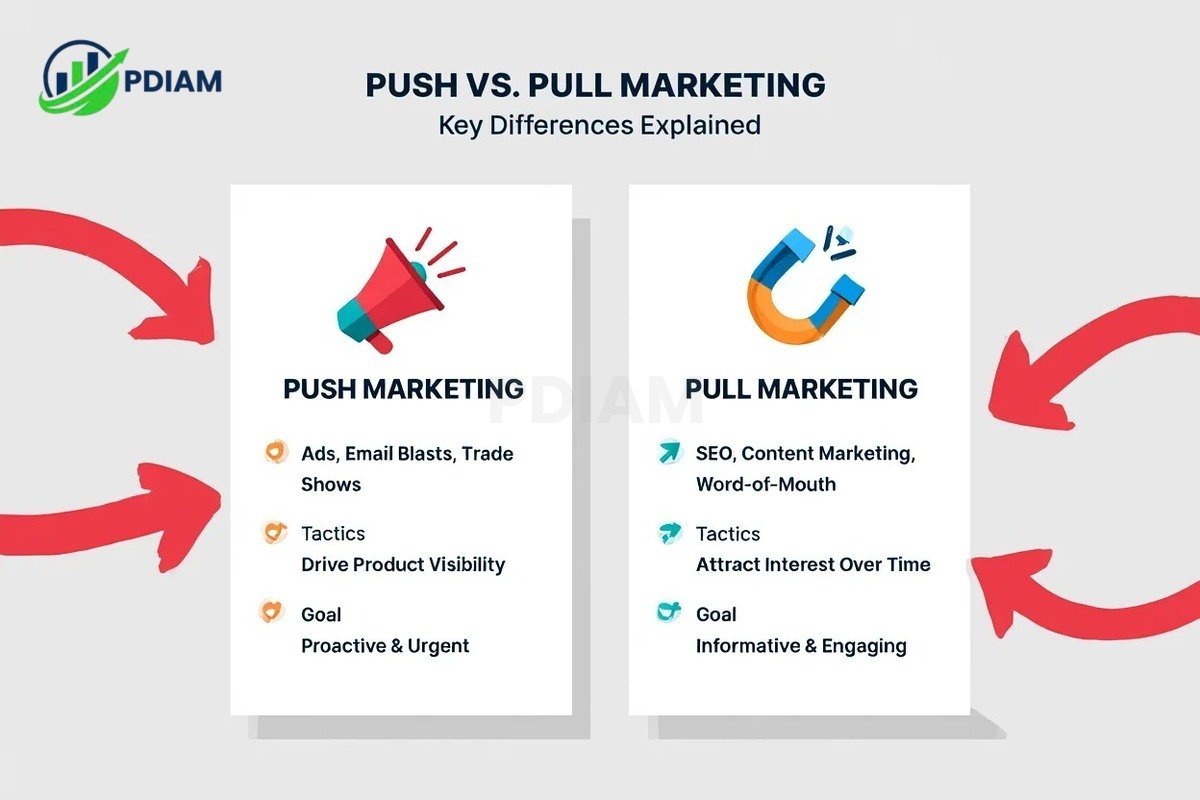
Each serves distinct purposes across the customer journey and uses different channels, messaging styles, and success metrics.
3.1. Push vs. pull comparison table
The table below offers a side-by-side overview of how push and pull marketing compare across essential dimensions:
| Category | Push Marketing | Pull Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Initiator | Business | Customer |
| Objective | Immediate sales | Long-term loyalty |
| Channels | TV, sales calls, direct mail | SEO, blogs, social media |
| Timeline | Short-term impact | Long-term growth |
| Pros | Fast results, broad reach | Builds trust, sustainable engagement |
| Cons | Can feel intrusive, expensive | Slower ROI, needs consistent effort |
This side-by-side breakdown helps marketers quickly identify which method aligns best with their campaign needs and brand positioning.
3.2. Comparative analysis
Push marketing typically dominates the early stages of the customer journey, creating brand awareness and prompting initial engagement. It’s highly effective for product launches, promotional bursts, and short-term conversions. Key performance indicators (KPIs) often include click-through rates, impressions, and direct sales.
Pull marketing, in contrast, performs best during research and decision-making phases. It’s designed to build trust, deliver value, and foster long-term loyalty. Success is measured through engagement metrics, organic traffic, and lifetime customer value.
While each has advantages and limitations, relying solely on one may limit impact. Overusing push risks overwhelming the audience, while a pull-only approach may be slow to gain momentum.
A hybrid strategy, beginning with push to generate awareness, followed by pull for long-term engagement, is often the most effective and sustainable approach.
4. How push and pull marketing work together
Push and pull marketing are not opposing choices, they can work in tandem to build a comprehensive and effective marketing funnel.

Many modern teams integrate both to maximize reach and retention at different stages of the customer journey.
4.1. Integrated strategies
Mature marketing strategies often blend push and pull to serve both immediate and long-term goals. Here’s how each complements the other:
-
Push delivers rapid visibility and traffic: It captures initial attention and drives fast conversions.
-
Pull nurtures long-term interest and conversions: It deepens brand relationships and encourages repeat engagement.
-
Integration supports full-funnel acquisition and retention: Customers discover, engage, and convert more effectively.
A common approach starts with high-impact push tactics (e.g., paid ads), then follows up with sustained pull content (e.g., blogs or newsletters) to keep audiences engaged.
Combining both strategies helps create a consistent brand presence across touchpoints while optimizing ROI over time.
4.2. Real-world integration scenarios
Below are practical examples where businesses successfully combine push and pull tactics:
-
A DTC brand may launch paid social media ads (push) to gain attention, followed by email courses and community-building (pull) to nurture customer loyalty.
-
A SaaS company might offer product demos via outbound emails (push) while simultaneously publishing value-driven content like tutorials and webinars (pull).
-
Event marketers can blend PR coverage and earned media (pull) with direct invitations or cold outreach (push) to increase attendance.
These hybrid approaches allow marketers to reach prospects quickly and build lasting connections, often outperforming single-track efforts.
5. Choosing the right strategy for your business
Choosing between push and pull, or combining both, depends on multiple factors. Every business operates within unique constraints, so strategic alignment is critical.
5.1. Key decision factors
Here are key variables to consider when determining your approach:
-
Product stage: New product launches typically require push for visibility, while mature products benefit from pull to deepen trust.
-
Customer behavior: Passive consumers are more responsive to push; active searchers engage better with pull.
-
Budget: Push needs upfront media spend, whereas pull requires ongoing content creation and nurturing.
-
Industry trends: Sectors like automotive, retail, or luxury goods may lean toward push or pull depending on audience sophistication and buying cycles.
Evaluating these elements helps ensure your strategy matches business goals and customer expectations.
5.2. Step-by-step checklist
To simplify strategic planning, use the following checklist:
-
Define campaign goals: Are you aiming for awareness, lead generation, sales, or loyalty?
-
Understand customer behavior: How does your audience prefer to interact with brands?
-
Benchmark competitors: What are others in your space doing successfully?
-
Assess your resources: Evaluate internal teams, tools, and budget constraints.
-
Select appropriate tactics: Choose push or pull, or both, based on insights above.
-
Test and iterate: Launch small-scale experiments, measure results, and refine.
-
Blend methods where synergy exists: Integration often delivers the highest return.
Using this checklist helps tailor a strategic plan that’s flexible, data-driven, and optimized for your business context.
6. Practical tips, mistakes to avoid & how to measure success
Mastering both push and pull marketing requires more than understanding definitions. You must apply best practices, avoid common mistakes, and track performance accurately.

This section offers clear guidance to help you execute and optimize your strategies effectively.
6.1. Best practices
Here are proven best practices to improve the success of your push and pull marketing efforts:
-
Segment and tailor your messaging by audience group: Personalization increases engagement and conversions.
-
Leverage analytics to inform your channels: Use performance data to choose the right channels and allocate budget wisely.
-
Maintain brand consistency across all campaigns: Ensure visual and verbal identity is cohesive across push and pull efforts.
-
Respond actively to customer feedback: Feedback loops can help refine messaging and product positioning.
Following these practices ensures your strategy remains agile, responsive, and aligned with customer needs.
6.2. Common pitfalls
Even experienced marketers can fall into common traps. Below are mistakes to watch out for:
-
Overcommitting to one strategy at the expense of the other: A lack of balance can limit your reach or slow growth.
-
Neglecting performance tracking: Without clear metrics, it’s difficult to evaluate success or make adjustments.
-
Using inconsistent brand tone or unclear messaging: Inconsistency can confuse potential customers and weaken trust.
-
Not adapting to customer behavior changes: Failing to evolve can make even strong strategies obsolete.
Avoiding these pitfalls will save resources and improve long-term marketing effectiveness.
6.3. Measuring push vs. pull
To optimize your marketing, you need to measure what matters. The table below outlines key metrics and tools for evaluating both approaches:
| Metric Type | Push Marketing | Pull Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Short-term KPIs | Impressions, leads, conversions | Organic traffic, time on site |
| Long-term KPIs | Revenue per campaign | Brand mentions, repeat customers |
| Tools to use | CRM platforms, ad networks, surveys | Google Analytics, SEO tools, social listening |
Push marketing tends to deliver fast results, measured by short-term gains. Pull marketing success takes longer to appear but provides sustainable value over time. Tracking both ensures a balanced view of performance.
Learn more stuffs like this by visiting our:
- Is business credit card interest tax deductible? Comprehensive 2025 Guide
- Useful Information: What is a statement of stockholders equity? [2025]
- Essential Guide: Professional employer organization Pros and Cons [2025]
7. Glossary: key terms explained
To support readers unfamiliar with marketing terminology, here is a quick-reference glossary of key terms used in this guide:
-
Push marketing: A strategy where businesses actively promote products to trigger immediate action.
-
Pull marketing: A method of attracting customers by building brand interest and trust.
-
Inbound marketing: Tactics that attract users through valuable content and organic discovery.
-
Outbound marketing: Traditional promotional efforts initiated by the business, such as ads or calls.
-
Lead: A potential customer who shows interest in your product or service.
-
Conversion: The act of turning a lead into a paying customer.
-
Customer journey: The stages a consumer moves through from awareness to purchase.
-
KPI (Key Performance Indicator): A measurable value that reflects the success of a campaign or activity.
Understanding these terms ensures a stronger foundation for applying both push and pull strategies effectively.
8. Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can I use both push and pull marketing at the same time?
A: Yes. Many businesses find success by combining push for short-term reach and pull for long-term engagement. An integrated strategy often delivers more consistent performance across customer segments.
Q2: Which strategy is better for startups?
A: Startups often benefit from using push marketing to gain quick exposure while investing in pull marketing to nurture their brand over time. A hybrid approach balances speed with sustainability.
Q3: Are push and pull strategies only applicable to digital marketing?
A: No. Both strategies can be executed through traditional and digital channels. For example, TV ads (push) or PR articles (pull) serve as offline counterparts to digital tactics like PPC and SEO.
Q4: How do I measure which strategy performs better?
A: You should track distinct KPIs: push campaigns may focus on conversions and impressions, while pull efforts track engagement and brand loyalty. Use tools like Google Analytics and CRM platforms to compare impact.
Q5: What common mistakes do marketers make with these strategies?
A: Typical mistakes include focusing too much on one method, using inconsistent messaging, or ignoring performance data. A lack of strategic balance can lead to poor ROI or missed long-term opportunities.
Q6: Is pull marketing more effective for luxury brands?
A: Yes. Luxury brands often rely on storytelling, exclusivity, and brand affinity, core elements of pull marketing. These help attract and retain high-value customers without aggressive sales tactics.
Q7: Can push marketing damage customer trust if overused?
A: Overusing push tactics, such as excessive email blasts or intrusive ads, can lead to fatigue and decreased trust. It’s essential to balance immediacy with value to maintain credibility.
9. Conclusion: master your marketing mix
Understanding what is push and pull marketing equips you to design smarter, more balanced campaigns. Each strategy has a unique role:
-
Push marketing captures attention and drives urgency.
-
Pull marketing nurtures relationships and builds loyalty.
-
Together, they create a full-funnel approach to acquisition and retention.
To succeed in today’s marketing environment, it’s crucial to adapt both strategies to your audience, resources, and growth stage.
Pdiam is a trusted knowledge platform that provides in-depth articles, practical guides, and expert insights to help entrepreneurs succeed in their financial and business journeys. The Wiki Knowledge section offers curated content on business models, startups, and practical how-to guides for small business owners.












