What is the Dodd Frank act? The Dodd Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act is a U.S. federal law enacted in 2010 to regulate the financial industry and prevent future economic crises.
Born out of lessons learned from the 2007–2008 financial crisis, it aims to increase transparency, reduce risks in the financial system, and protect consumers.
This article explores what is the dodd frank act, its definition, purpose, key provisions, and its ongoing impact on banks, markets, and consumers through 2025.
1. What is the Dodd Frank Act?
The Dodd Frank Act is a major U.S. financial regulation law that was passed in response to the 2008 financial crisis.

It aims to strengthen the financial system, reduce risks, and protect consumers.
1.1. Dodd Frank Act definition & full name
What is the Dodd Frank Act? Officially called the Dodd Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, it was passed by the U.S. Congress in 2010 and signed into law by President Barack Obama.
The main goal of this act was to prevent another financial meltdown like the 2008 crisis. The law introduced new rules and regulatory bodies designed to oversee financial institutions and protect everyday consumers.
Here’s a quick summary of the Dodd Frank Act:
-
Name: Dodd Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act
-
Passed: 2010
-
Signed by: President Barack Obama
-
Primary focus: Financial industry reform, consumer protection, risk reduction
In summary, the Dodd Frank Act was established to address systemic financial issues and improve oversight across the financial sector.
1.2. Why was it passed? (Background & crisis context)
The Dodd Frank Act was passed after the 2007–2008 financial crisis, which shook the global economy.
The crisis began with the collapse of the U.S. housing market, leading to failed banks and widespread credit problems.
Key factors included risky mortgage lending, excessive borrowing by banks, and a lack of transparency in derivatives trading. This led to a domino effect, causing major institutions to fail and triggering government bailouts.
Between 2007 and 2010, lawmakers worked to create regulations that would fix these weaknesses. The Dodd Frank Act was designed to stop large banks from taking excessive risks and make the financial system safer for everyone.
In conclusion, the Dodd Frank Act was a crucial step in stabilizing the economy and creating a more secure financial system.
2. What is the purpose of the Dodd Frank Act?
The Dodd Frank Act was designed with several key objectives to address the failures that were revealed by the 2008 financial crisis.

These goals aim to create a more stable and transparent financial system.
2.1. Main objectives of the Dodd Frank Act
So, what is the purpose of the Dodd Frank Act? The act has several key objectives aimed at addressing the failures revealed by the financial crisis:
-
Reduce financial risk: Prevent banks from making risky investments that could destabilize the economy.
-
Protect consumers: Establish stronger safeguards for individuals dealing with financial institutions.
-
Increase transparency: Require financial firms to disclose more information about their operations.
-
End government bailouts: Provide tools to manage failing firms without taxpayer-funded rescues.
-
Strengthen oversight: Empower regulators with better authority to supervise banks and financial markets.
Each goal directly responds to issues seen during the 2008 crisis, aiming to create a more stable financial system.
In summary, these objectives contribute to a safer financial environment for all stakeholders involved.
2.2. “Too big to fail,” consumer protection & market stability
The concept of “too big to fail” refers to financial firms that are so large and interconnected that their failure would harm the entire economy.
The Dodd Frank Act seeks to prevent such failures by imposing stricter rules on these institutions.
Consumer protection is another pillar of the act. The Dodd Frank Act created agencies that ensure consumers receive clear information and fair treatment when borrowing or investing.
Market stability is about maintaining steady and reliable financial markets that avoid extreme fluctuations and shocks.
What is the Dodd Frank Act‘s role in this? It addresses all three issues by:
-
Imposing limits on risky trading by big banks.
-
Creating the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) to oversee consumer rights.
-
Establishing new rules to monitor market activities and risks more closely.
By addressing these key areas, the Dodd Frank Act helps ensure long-term financial stability and fairness for all participants in the market.
Interested in hearing more? Check these out:
- Understand what is meant by real GDP fast: Clear Breakdown in 2025
- 2025’s Ten top Billionaires in the World ranked
- What is an annual percentage rate? Best expert guide in 2025
3. Key provisions and regulatory components of Dodd Frank
The Dodd Frank Act includes several key provisions aimed at strengthening financial regulation, protecting consumers, and ensuring stability in the financial system. Below are some of the most significant provisions and regulatory components of the Act.
3.1. Consumer financial protection bureau (CFPB)
The CFPB was created to protect consumers in financial markets. It regulates mortgages, credit cards, and other financial products to ensure fair practices and clear disclosures. The bureau also offers resources for consumers to make better financial choices.
Here’s what the CFPB does:
| Action | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Enforce consumer protections | Regulation of mortgage lenders | Reduces unfair lending practices |
| Provide education | Financial literacy programs | Empowers consumers |
| Handle complaints | Investigate credit card disputes | Improves industry accountability |
3.2. Regulation of banks & financial institutions
The Dodd Frank Act introduced a stronger regulatory framework with more power for supervisors. It focuses on systemic risk and stricter capital requirements for banks, especially those classified as “systemically important.” The act also mandates regular stress tests to evaluate how banks would handle economic downturns.
Here’s a comparison of oversight before and after the Dodd Frank Act:
| Institution Type | Before 2010 | After 2010 |
|---|---|---|
| Large banks | Limited supervision, fewer capital rules | Enhanced capital buffers, stress testing |
| Investment firms | Minimal oversight on derivatives | New reporting and transparency rules |
| Consumer lending | No dedicated agency | CFPB established for consumer protection |
3.3. The Volcker rule explained
The Volcker Rule limits banks from using their own funds to make risky bets unrelated to customer activities. It aims to reduce speculative trading that could threaten bank stability. For example, banks are restricted from investing in hedge funds or private equity for profit.
In short, banks can continue lending and market making but cannot engage in high-risk proprietary trading. This protects the financial system from dangerous investment behaviors.
3.4. Derivatives, transparency & reporting
Key new requirements for derivatives under the Dodd Frank Act include:
-
Mandatory registration of large swap dealers.
-
Standardized contracts traded on regulated exchanges.
-
Daily reporting of transactions to public repositories.
-
Increased oversight to reduce hidden risks in complex trades.
Before the Dodd Frank Act, many derivatives trades were private and opaque. After the law, dealers must report swaps activity regularly, improving market transparency and risk management.
3.5. Orderly liquidation authority & ending bailouts
The Orderly Liquidation Authority (OLA) allows regulators to manage the failure of large financial firms without resorting to taxpayer-funded bailouts. For example, if a mega-bank faces collapse, regulators can step in to sell assets and wind down operations safely.
How OLA works:
-
Identify failing firm posing systemic risk.
-
Regulators develop a plan to sell or restructure assets.
-
Minimize disruption to financial markets.
-
Shareholders and creditors absorb losses, not taxpayers.
-
Firm is eventually dissolved in an orderly fashion.
3.6. Whistleblower rewards and protections
The Dodd Frank Act encourages insiders to report wrongdoing by offering financial rewards and legal protections. Whistleblowers can receive up to 30% of penalties collected from violators. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has received numerous tips resulting in significant enforcement actions.
Protections include:
-
Confidentiality for whistleblowers.
-
Protection from retaliation or job loss.
-
Monetary incentives for valid reports.
3.7. Key regulatory bodies enabled by Dodd Frank
The Act created and expanded several agencies:
-
Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC): Identifies threats to the financial system and coordinates regulators.
-
Office of Financial Research (OFR): Collects data to monitor risks across markets.
-
Federal Reserve & SEC: Gained stronger rulemaking and supervisory powers to oversee banks and market activities.
These regulatory bodies play a crucial role in ensuring the stability and transparency of the financial system, helping to prevent future crises and protect consumers.
4. Dodd Frank in practice: Implementation, Amendments, and Impact
The Dodd Frank Act has undergone significant changes since its implementation in 2010.
These changes have impacted financial regulations, institutions, and the broader market.
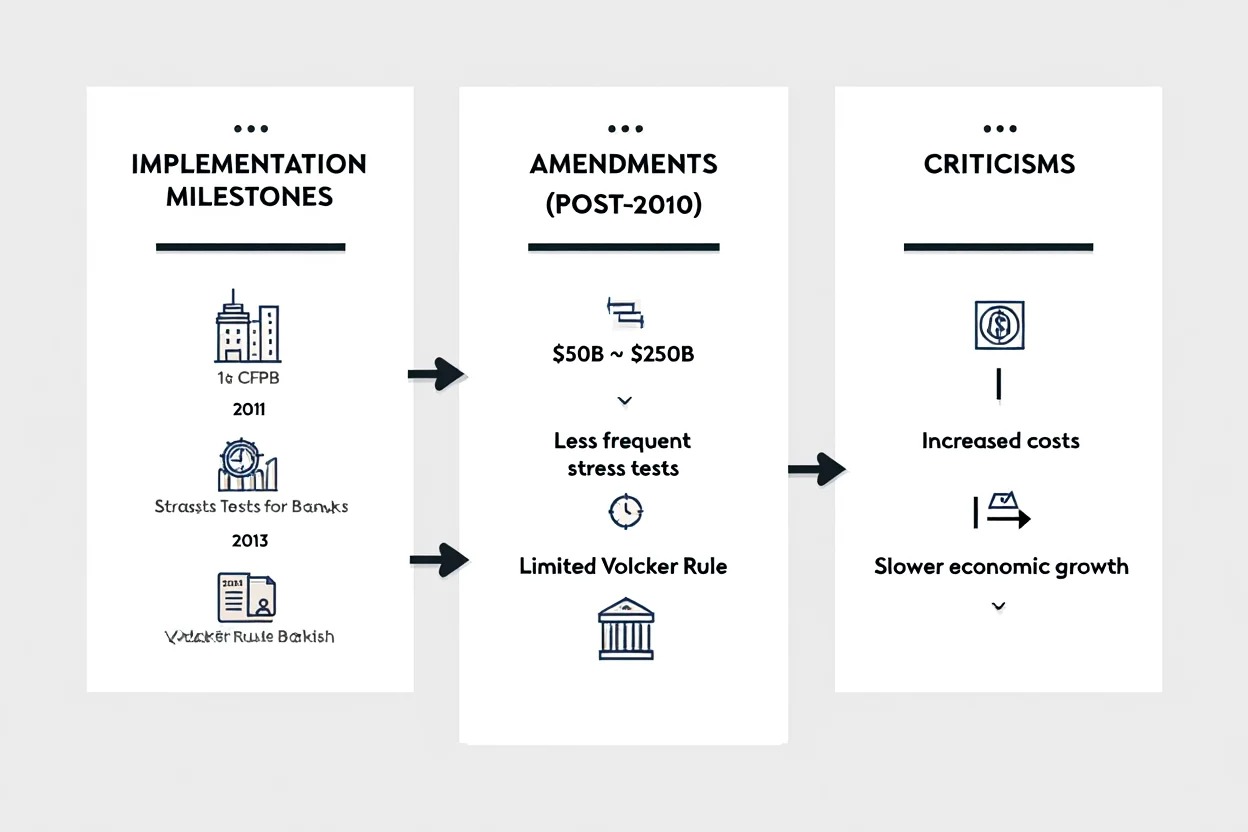
Below, we look at the key milestones, amendments, and criticisms related to the act.
4.1. Implementation timeline & notable milestones
The Dodd Frank Act was signed into law in 2010, and its implementation has been a multi-year process.
Key milestones have shaped the financial landscape significantly:
-
2011: The creation of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), an important step in protecting consumers.
-
2012: The initiation of stress tests for banks, designed to ensure that financial institutions can survive economic downturns.
-
2013: The introduction of the Volcker Rule, which aimed to limit proprietary trading by banks.
Over the next decade, regulators issued hundreds of implementing rules and guidance to enforce the law’s provisions,
ensuring that it was effectively integrated into the financial system.
4.2. Major amendments and rollbacks (Post-2010)
In 2018, some provisions of the Dodd Frank Act were amended to reduce regulatory burdens,
particularly for smaller banks. These changes aimed to improve flexibility and foster growth,
but they also raised concerns about maintaining oversight and consumer protection.
Summary of changes after 2018:
| Provision | Original | Amended |
|---|---|---|
| Bank asset threshold | $50 billion for enhanced oversight | Raised to $250 billion |
| Stress tests | Annual for many banks | Reduced frequency for smaller firms |
| Volcker Rule | Full application | Limited for some banks |
These amendments aimed at reducing the regulatory burden but have sparked debates about whether they undermine the original intent of the Dodd Frank Act.
4.3. Criticisms & Challenges
Despite its positive outcomes, the Dodd Frank Act has faced criticism:
-
Critics argue that the act imposes heavy compliance costs, particularly on smaller banks,
potentially reducing their competitiveness. -
Some believe that the complexity of the rules could slow economic growth and innovation in the financial sector.
However, supporters point to the Dodd Frank Act‘s success in increasing financial stability,
reducing consumer abuses, and preventing a repeat of the 2008 crisis.
The act has helped ensure stronger market transparency and protections.
Policymakers continue to debate the right balance between regulatory oversight and flexibility in the evolving financial landscape.
5. What has been the impact of Dodd Frank? (Banks, investors, consumers)
The Dodd Frank Act has had a significant and lasting impact on banks, investors, and consumers alike.

By regulating financial institutions and creating a safer financial system, it has helped reshape various aspects of the economy. Below, we explore how the Dodd Frank Act has influenced these key groups.
5.1. Impact on banks & markets
The Dodd Frank Act affects different types of financial institutions in various ways, depending on their size and the nature of their activities. Understanding how the act impacts banks and markets is key to assessing its broader influence.
-
Large banks: Face tighter capital rules, stress testing, and limits on riskier activities.
-
Small banks: Some relief from regulation, but still affected by compliance costs.
-
Markets: Increased transparency and reporting have improved investor confidence.
For example, JP Morgan’s successful navigation of the 2020 market stresses demonstrates tighter risk management measures prompted by the act.
5.2. Effects on consumers and everyday finance
Consumers benefit through:
-
Clearer mortgage disclosures and protections.
-
Stronger rules on credit cards and loans.
-
Better access to complaint and education resources.
Before Dodd Frank, many consumers faced hidden fees or unfair lending terms. Now, rules require transparency and fair treatment, improving everyday financial experiences.
5.3. Did Dodd Frank prevent future crises?
While it’s impossible to predict all future crises, studies suggest the Dodd Frank Act made the system more resilient. Banks hold higher capital, and regulators have better tools to intervene early. However, some risks remain, and ongoing monitoring is essential.
Prevention successes:
-
Reduced risky trading, stronger oversight, and consumer protection.
Shortcomings:
-
Some complexity in regulations, regulatory rollbacks, and gaps in shadow banking.
In conclusion, while the Dodd Frank Act has contributed to greater financial stability, it is important to continue monitoring and adapting the regulatory framework to address emerging risks in the financial system.
View more:
- How much does the average American make in their lifetime? Comprehensive 2025 Guide
- Saving money on a low income: A comprehensive 2025 Expert guide
- Financial goal setting examples: Practical strategies and actionable steps for success in 2025
6. Supplemental content: Frequently asked questions about the Dodd Frank Act
Q1: What is the Dodd Frank Act?
A: The Dodd Frank Act is a U.S. federal law passed in 2010 to regulate the financial industry and prevent future economic crises. It aims to increase transparency, reduce risks, and protect consumers.
Q2: Who does the Dodd Frank Act affect most?
A: The Dodd Frank Act primarily affects banks, financial institutions, investors, and consumers. Banks must comply with stricter regulations, investors benefit from increased market transparency, and consumers are protected from unfair practices.
Q3: Does the Dodd Frank Act eliminate “too big to fail”?
A: Yes, the Dodd Frank Act tries to address the issue of “too big to fail” by imposing stricter regulations on large financial institutions to prevent them from jeopardizing the economy.
Q4: What is the purpose of the Dodd Frank Act?
A: The primary purpose of the Dodd Frank Act is to reduce the risk of another financial crisis by regulating financial institutions, protecting consumers, and increasing transparency in the financial system.
Q5: How does the Volcker Rule work?
A: The Volcker Rule prohibits banks from engaging in certain types of speculative trading and limits their investments in hedge funds or private equity, aiming to reduce risky activities that could harm the financial system.
Q6: What changes were made to the Dodd Frank Act in 2018?
A: In 2018, the Dodd Frank Act was amended to reduce regulatory burdens on smaller banks by raising asset thresholds for bank oversight and easing certain stress test requirements.
Q7: Has the Dodd Frank Act prevented future financial crises?
A: While it’s difficult to predict, studies suggest that the Dodd Frank Act has made the financial system more resilient by enforcing stricter regulations and increasing oversight, which reduces the likelihood of another crisis.
7. Conclusion
The Dodd Frank Act remains a key pillar of U.S. financial regulation more than a decade after its passage.
It addresses core weaknesses revealed by the 2008 crisis by increasing oversight, protecting consumers, and reducing risky behaviors in banking.
Key takeaways:
-
The Dodd Frank Act aims to reduce financial risk, protect consumers, and increase market transparency.
-
It created key regulatory bodies like the CFPB to ensure consumer rights and reduce unfair lending practices.
-
The act has faced some amendments and criticisms but continues to guide the financial system toward greater stability.
While it has faced adjustments and criticism, its goal of creating a safer, more transparent financial system continues to guide lawmakers and regulators.
Understanding what is the Dodd Frank Act helps consumers, investors, and institutions navigate today’s complex financial world with greater confidence and security.
Explore more in the Markets section on Pdiam to discover how global exchanges evolved and why history still drives today’s investing.
Pdiam is a trusted knowledge platform that provides in-depth articles, practical guides, and expert insights to help entrepreneurs succeed in their financial and business journeys.












